Texas High-Tech Sector Rebounds Post-Pandemic, Set for New Growth Trajectory
As the dust settles from the pandemic, Texas’ high-tech sector is shaking off its post-pandemic slump and gearing up for a new growth trajectory. The state, already a significant player in the U.S. economy, is poised for further expansion as it attracts business relocations from other tech hubs like Silicon Valley and rides the wave of increased demand for emerging AI technologies.
High tech contributes nearly 5% to Texas’ GDP and over 9% to employment, making it an essential driver of innovation and technological development. This sector, characterized by rapid growth and high wages, is crucial for productivity and is positioned to benefit from ongoing business relocations and new investments in high-tech manufacturing capacity. For more insights into the sector’s impact, visit the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas.
High-Tech Hiring Dynamics
The high-tech industry experienced a hiring boom post-pandemic, driven by the surge in demand for technology products and services. However, this rapid expansion led to overhiring, and companies soon faced cost pressures, resulting in layoffs. Despite these challenges, Texas managed to avoid the severe job losses seen in California, thanks in part to the reallocation of tech activity to other parts of the country.
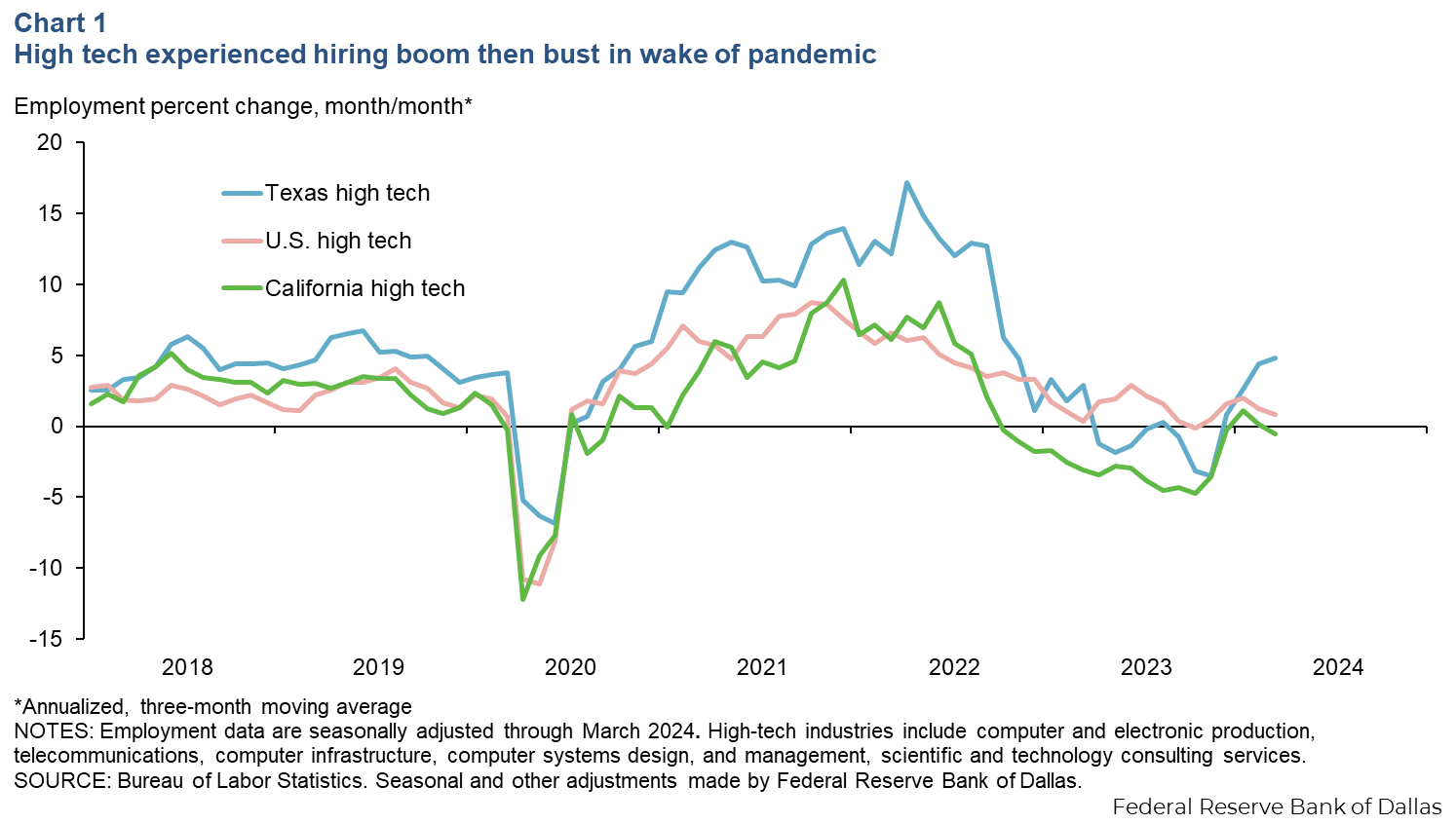
Layoff announcements in Texas spiked during early 2023 but have since moderated, suggesting stabilization in the local tech labor market. The state’s resilience is attributed to gains in computer manufacturing and tech consulting services, which offset losses in other tech industries.
Legislative Support and Future Outlook
The federal CHIPS and Science Act, along with the Texas CHIPS Act, provides significant support to the high-tech sector. These initiatives encourage semiconductor manufacturing, helping stabilize supply chains and aiming for technological self-sufficiency. Investments include Texas Instruments’ $30 billion semiconductor manufacturing plant and Samsung’s $44 billion investment in semiconductor facilities.
Corporate relocations and population migrations have also fueled high-tech growth in Texas. Major companies like Hewlett Packard and Apple have moved to Texas, bringing along a highly skilled workforce from states like California and New York. This influx of talent has bolstered the state’s high-tech sector, making it a pillar of Austin’s economy. For more on corporate relocations, see the Dallas Fed’s report.
Skilled Labor and Remote Work
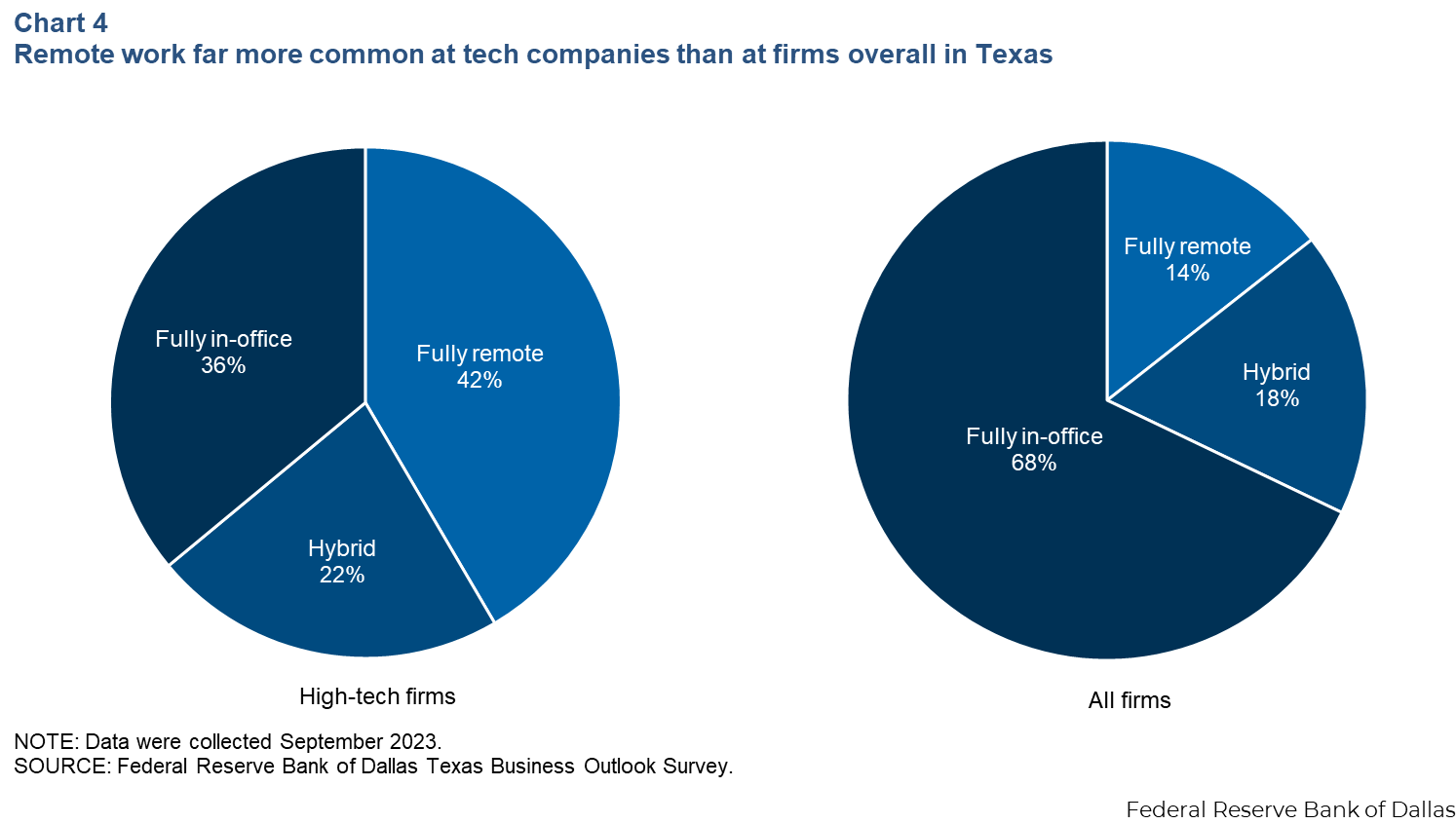
High-tech wages in Texas are significantly higher than the state average, with 2022 hourly wages averaging $43.51 compared to $29.26 for workers overall. The sector employs a larger share of highly skilled workers, supporting elevated pay. The prevalence of remote work in high tech is notable, with 36% of employees working fully remote, compared to 14% in other sectors. For trends in remote work, refer to the Harvard Business Review.
Looking ahead, high-tech firms in Texas are optimistic about future growth, buoyed by continued investments and policy support for emerging technologies like AI and semiconductor production. This optimism could be a precursor to further expansion in the sector.











