Exploring Real Estate Investment: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring Real Estate Investment: A Comprehensive Guide
Real estate investment is a popular avenue for diversifying one’s portfolio and generating passive income. However, the traditional notion of becoming a landlord—complete with calls about leaky faucets and pest control—might not appeal to everyone. Fortunately, as highlighted in a recent NerdWallet article, there are various strategies to invest in real estate without the hassle of direct property management.
-
Invest in REITs
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) offer an accessible entry into the world of real estate. These entities own and manage a portfolio of real estate assets. They are akin to mutual funds and often pay high dividends, making them a favorite for retirement portfolios. New investors are advised to start with publicly traded REITs for ease of liquidity and valuation.
-
Utilize Online Real Estate Platforms
Platforms like Fundrise and RealtyMogul connect investors with developers seeking project financing. While these options can yield regular distributions, they are often open only to accredited investors, as defined by the SEC.
-
Consider Rental Properties
Buying and renting out properties can be lucrative. The concept of “house hacking,” popularized by BiggerPockets, involves living in a property while renting out parts of it to cover expenses. This approach can provide valuable industry insights, though it may require hiring a property manager if you prefer a hands-off role.
-
Flip Properties
Flipping properties involves purchasing undervalued homes, renovating them, and selling for a profit. While popularized by TV shows, this strategy carries risks, particularly if repair costs are underestimated. Partnering with experienced contractors can mitigate some of these risks.
-
Rent Out a Room
For those new to real estate, renting out a room in your home can be a gentle introduction. This arrangement can reduce housing costs and make mortgage payments more manageable. Platforms like Airbnb provide an opportunity for short-term rentals without the commitment of a long-term tenant.
Each investment strategy comes with its own set of challenges and rewards. As the NerdWallet article suggests, the best approach depends on your financial goals, available capital, and willingness to manage property-related issues. For those lacking DIY skills, REITs or crowdfunding platforms might be preferable to direct property investments.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
More Articles
Getting licensed or staying ahead in your career can be a journey—but it doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Grab your favorite coffee or tea, take a moment to relax, and browse through our articles. Whether you’re just starting out or renewing your expertise, we’ve got tips, insights, and advice to keep you moving forward. Here’s to your success—one sip and one step at a time!
Autonomous Vehicles and Their Economic Impact: A Look into the Future of Mobility
Autonomous Vehicles: Driving the Future of Urban Mobility and Economic Growth
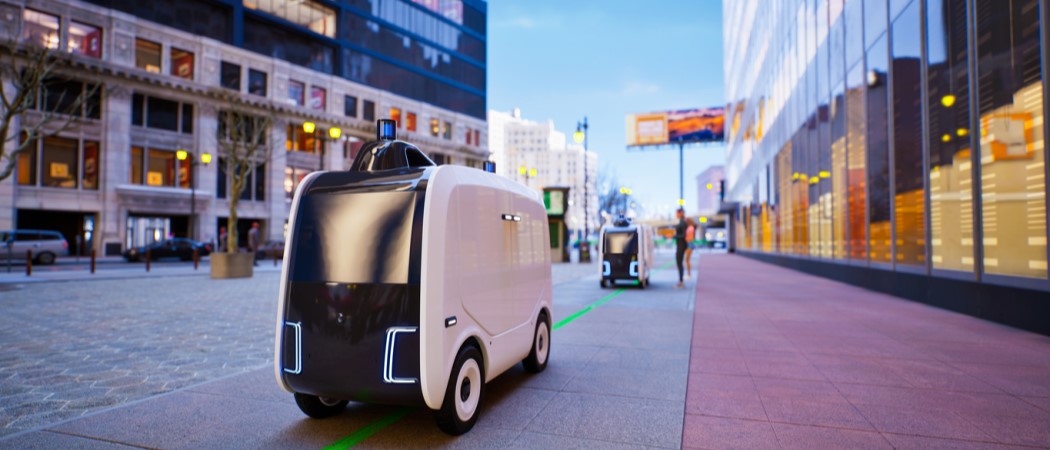
The recent enactment of the Automated Vehicles Act in the UK heralds a new era for transportation, with self-driving vehicles expected to hit the roads by 2026. This legislative milestone is poised to revolutionize how people and goods move across the nation, potentially transforming urban spaces and transport systems as we know them.Economic Impact and Societal Interactions Understanding the intersection between autonomous vehicles (AVs) and society is crucial for assessing their economic impact. According to a study referenced by the Economics Observatory, the potential economic benefits in the UK could reach £51 billion by 2030. These gains stem from consumer savings, reduced travel time, and improved safety. The UK government is actively exploring policies to ensure AVs support sustainable economic growth and contribute to the transition to net-zero emissions.
Transforming Transport and Logistics The transport and logistics sectors are expected to be early adopters of AV technology, driven by the promise of reduced costs and increased efficiency. The elimination of human drivers could significantly cut labor expenses, while AVs’ ability to operate 24/7 could enhance productivity and customer satisfaction. Moreover, AVs could optimize delivery routes, addressing last-mile delivery challenges and improving customer experiences. Autonomous drones and robots, for example, could deliver packages to remote locations lacking proper transport infrastructure.
Personal Mobility and Social Inclusion AVs hold the potential to improve personal mobility, particularly for individuals underserved by current transport systems, such as the elderly and those with disabilities. By reducing transport costs, AVs could enhance mobility for middle and lower-income groups, fostering social inclusion and enabling access to employment and leisure activities. Fleet-based shared automated vehicles could offer low-cost, on-demand services, complementing traditional public transport and improving first- and last-mile connections.
Challenges and Opportunities Despite their benefits, AVs are expected to disrupt employment in sectors like public transport and delivery services, potentially leading to job losses. Policymakers must focus on education and retraining programs to help displaced workers transition to new roles. Additionally, AVs could exacerbate urban sprawl as individuals choose to live further from urban centers due to reduced transport costs and improved connectivity.
Driving Economic Growth AVs could significantly boost productivity by reducing travel costs and enhancing connectivity between urban centers and their peripheries. This improved accessibility could lead to job and population relocations, fostering agglomeration economies and increasing firms’ productivity. A study for the United States suggests that AVs could increase GDP by $214 billion and create 2.4 million new jobs.
Environmental Sustainability AVs offer the potential to optimize fuel consumption and reduce carbon emissions, contributing to a more sustainable transport system. By integrating electric and hybrid vehicles, AVs could further minimize greenhouse gas emissions, aiding in climate change mitigation efforts.
Addressing Concerns and Building Trust For AVs to gain public acceptance, companies and governments must address concerns about safety, reliability, and cybersecurity. Establishing robust security measures and transparent communication will be critical in fostering public trust. The UK government’s proactive approach to regulating AVs, as outlined in their regulation plan, sets a precedent for ensuring safety and legal clarity.
 Conclusion
The advent of autonomous vehicles represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of urban mobility and economic growth. As the UK prepares for their integration into public roads, addressing challenges and leveraging opportunities will be essential in shaping a smarter, more connected future.
Conclusion
The advent of autonomous vehicles represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of urban mobility and economic growth. As the UK prepares for their integration into public roads, addressing challenges and leveraging opportunities will be essential in shaping a smarter, more connected future.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
AI in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Medicine or Overhyped Promise
Current Advancements
AI has already demonstrated its prowess in several areas. Notably, it expedited the development of mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 and is now being harnessed to create new protections against a variety of diseases. Generative AI, akin to ChatGPT, is also paving the way for new immunotherapy drugs.
In diagnostics, AI’s ability to analyze medical scans and records is proving invaluable. The American College of Surgeons notes that AI often surpasses radiologists in interpreting scans, identifying subtle signs of diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.
Challenges and Caution
Despite these successes, AI in healthcare is not without its challenges. A study on pulmonary embolism highlighted AI’s potential to reduce hospital stays, yet not all AI applications have been as effective. The discontinuation of IBM’s Watson Health partnership with MD Anderson Cancer Center due to accuracy issues serves as a cautionary tale.
Moreover, symptom-checker tools, which sometimes rely on AI, have been criticized for their low accuracy, posing potential safety risks. Additionally, the promise of administrative efficiencies through AI remains largely unrealized, with little evidence of significant cost savings or improvements in patient care.
Expert Opinions
Experts offer a range of perspectives on AI’s future in healthcare. Dr. Eric Topol, author of Deep Medicine, acknowledges AI’s utility in certain applications but emphasizes the irreplaceable value of human interaction in patient care. He envisions a future where AI augments rather than replaces human skills, enabling doctors to spend more time with patients.
Dr. Fei-Fei Li from Stanford University echoes this sentiment, highlighting AI’s role in alleviating administrative burdens, thereby restoring the “human element” to medicine. However, an article in MIT Technology Review warns against over-reliance on AI, particularly when trained on biased data, which could lead to inequities in care.
The Path Forward
While AI holds the promise of transforming healthcare, it is not a panacea. The early successes in drug discovery and diagnostics are promising, yet challenges such as data privacy, cost, and training must be addressed. The consensus among professionals is that AI should enhance human expertise, not replace it.
For technology companies, the key to driving meaningful change lies in developing AI applications that complement human skills, thereby delivering tangible benefits to healthcare systems and patients alike.

Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies: A New Era in Finance
Countries around the globe, from the Bahamas to China, are actively exploring or have already initiated CBDC projects. The primary objective is to enhance financial inclusion, offering secure and efficient payment options for those without access to traditional banking systems. As noted in a report by the U.S. Federal Reserve, CBDCs have the potential to significantly reduce cross-border transaction costs, bolster the international standing of dominant currencies like the dollar, and simplify access to financial services.
However, this shift to digital currencies also presents several challenges. Privacy concerns, potential cybersecurity threats, and the impact on existing banking structures are critical issues that need careful consideration. Ensuring robust cybersecurity frameworks and balancing transaction monitoring to prevent financial crimes are essential steps in this journey.
CBDCs are categorized into two main types: wholesale and retail. Wholesale CBDCs are typically used by financial institutions for interbank transactions, while retail CBDCs are consumer-focused, allowing potentially anonymous transactions using public or private keys.
While smaller nations like Jamaica, Nigeria, and the Bahamas have already implemented CBDCs, larger economies and groups like the G20 are still in the exploratory stages, assessing the implications for monetary policy and financial stability.
For more in-depth information, the original article can be found on Investopedia.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Ethical Maze of AI in Radiography: A Saudi Arabian Perspective
The Ethical Maze of AI in Radiography: A Saudi Arabian Perspective
In an era where artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping the landscape of healthcare, a recent study published in BMC Medical Ethics sheds light on the intricate ethical challenges radiographers face as they navigate AI integration in radiography. Conducted in Saudi Arabia, this cross-sectional study delves into the perspectives of radiographers, revealing a tapestry of enthusiasm and apprehension towards AI’s role in their field.The research, available on the BMC Medical Ethics website, highlights the transformative opportunities AI presents for diagnostic imaging, alongside the ethical considerations that accompany its adoption. Through a structured questionnaire, radiographers shared their insights on AI’s ethical implications, emphasizing the need for transparency, patient privacy, and the establishment of ethical guidelines.
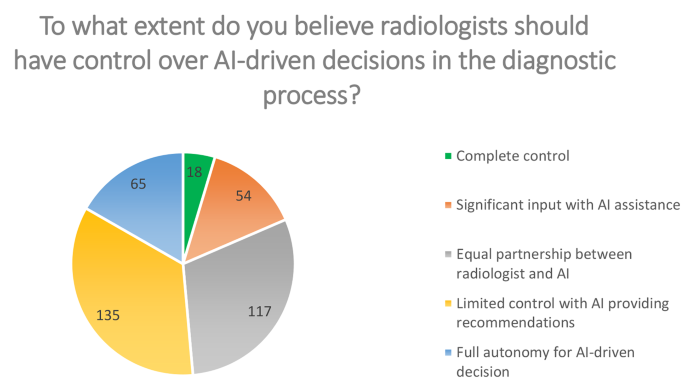
Unfamiliar Terrain
The study reveals a significant portion of radiographers are unfamiliar with AI’s integration into their practice, with many expressing uncertainty about the importance of AI transparency. However, a notable number advocate for AI systems that provide justifications for their decision-making processes, highlighting a desire for clarity in AI operations.Ethical Dilemmas and Patient Privacy
Radiographers voiced concerns about ethical dilemmas that AI might introduce, with nearly half agreeing that AI could exacerbate these challenges. Patient privacy emerged as a critical issue, with a substantial portion of participants expressing apprehension about AI’s impact on confidentiality. These findings underscore the necessity for specific ethical guidelines to govern AI use in radiography.Guiding the Future
The study calls for the development of robust ethical frameworks, educational improvements, and policy enhancements to ensure AI technologies are implemented safely and ethically. These measures aim to maximize diagnostic benefits while minimizing ethical risks, providing a roadmap for policymakers and practitioners to navigate the evolving AI landscape in healthcare.For further insights into the study and its implications, visit the BMC Medical Ethics Journal.
CSS Styling
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Telehealth Revolution: Transforming the Healthcare Landscape
Telehealth: A New Era in Healthcare
Telehealth has dramatically transformed healthcare delivery, offering increased accessibility and reshaping patient care. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated its adoption, with the U.S. experiencing a 154% surge in telehealth visits in March 2020. This adaptability is mirrored in mental health services, where telepsychiatry has become essential for continuous patient support, especially in remote areas.Financially, telehealth presents significant cost-saving opportunities by reducing non-urgent emergency visits. A McKinsey report suggests that up to $250 billion of U.S. healthcare spending could be virtualized.
Beyond Healthcare: Cross-Industry Applications
Telehealth technology extends its benefits beyond healthcare. In education, it bridges the gap between medical knowledge and practical application, enhancing clinical skills through simulation training. Platforms like Project ECHO facilitate knowledge sharing among healthcare professionals.In the corporate world, telehealth is integral to wellness programs, providing employees with convenient access to health services. This integration boosts productivity and reduces healthcare costs, as noted by the National Business Group on Health.
Technological Integration: No-Code and Low-Code Platforms
The rise of No-Code (NC) and Low-Code (LC) platforms is reshaping operational dynamics in healthcare. These platforms allow for the rapid development and deployment of digital solutions, making technology more accessible. According to a Healthcare Management Review study, they can accelerate clinical application development by 50-70%, reducing costs and improving efficiency.Personalization and Future Prospects
Personalizing telehealth services enhances patient satisfaction and engagement. Studies show that personalized interventions improve outcomes in chronic disease management, such as diabetes. AI and wearable technologies are advancing diagnostic precision and real-time monitoring, paving the way for more effective care.As we move into 2024, the integration of telehealth, AI, and wearables promises to set new benchmarks for accessible and personalized healthcare services. This evolution points towards a more connected, health-conscious future, as detailed in the original article.

Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Electric Vehicle Market Surges Amidst Economic and Environmental Challenges
Electric Vehicle Market Surges Amidst Economic and Environmental Challenges
The global electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing a remarkable transformation, driven by a combination of technological advancements, policy incentives, and growing environmental awareness. According to a report by the TRENDS Research & Advisory, sales of battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) soared beyond 10 million in 2022, marking a 55% increase from the previous year. This surge underscores the rapid adoption of EVs despite challenges such as supply chain disruptions and fluctuating energy prices.
The Global EV Outlook 2023 by the International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights the pivotal role of government policies in this growth. The Electric Vehicles Initiative (EVI), established under the Clean Energy Ministerial, has been instrumental in promoting zero-emission government fleets, further accelerating the shift towards sustainable transport solutions.
Global Trends and Policy Efforts
In line with the IEA’s Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS), the global share of EV sales is projected to reach 35% by 2030, with China, the United States, and Europe leading the charge. This growth trajectory is bolstered by strategic legislation and expanding battery manufacturing capacities, aimed at meeting the rising demand for EVs.
Despite these positive trends, the market faces hurdles such as the high cost of EVs, limited charging infrastructure, and battery technology challenges. To address these issues, governments and private entities are investing in innovative business models and enhanced charging networks, as emphasized in Fayez Alanazi’s research on EV adaptation.
Environmental and Economic Implications
Electric vehicles are heralded as a crucial solution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, a sentiment echoed in the Gemopai report. EVs offer zero tailpipe emissions, contributing significantly to cleaner air and a reduction in the carbon footprint of transportation.
However, the economic rationale for EV adoption is complex. A study by David S. Rapson and Erich Muehlegger from the National Bureau of Economic Research explores the balance between operational savings and the upfront costs of EVs. The study suggests that while subsidies and incentives are crucial, they must be tailored to regional energy policies and market dynamics to maximize their impact.
The Future of Electric Mobility
The hybrid vehicle market is also experiencing growth, with projections indicating a 14% increase by 2031. This trend, highlighted by Fact.MR, reflects a shift in consumer preferences towards eco-friendly transportation options, driven by rising environmental consciousness and fuel efficiency demands.
Looking ahead, the EV market is poised for substantial expansion, with forecasts predicting a market size of $56.7 trillion by 2050, as reported by Nasdaq. This growth is expected to transform the automobile and energy sectors, with Chinese manufacturers leading the charge in EV production and innovation.
Conclusion
The path to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 is intricately linked to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. As highlighted by McKinsey & Company, this transition presents both opportunities and challenges for automakers and policymakers alike. By navigating these complexities and fostering collaboration across sectors, the electric vehicle industry can drive meaningful progress towards a sustainable and low-carbon future.
“`Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
UAE’s Vision for Desert Expansion and Urban Innovation
UAE’s Vision for Desert Expansion and Urban Innovation
In a bold move to accommodate its rapidly growing population, the UAE is set to transform its expansive desert landscapes into thriving residential communities. This strategic development aligns with the nation’s commitment to harnessing natural resources and implementing the ’15-minute city’ model. This urban planning concept aims to make essential amenities accessible within a short walk, enhancing city life and promoting climate resilience.

Population Surge and Urban Planning
The population of Dubai is projected to nearly double by 2040, driven by its dynamic economy and global connectivity. According to the Dubai Statistics Centre, approximately 25,700 people relocated to the city in the first quarter of 2024. Other cities, including Abu Dhabi, Ras Al Khaimah, and Sharjah, are also experiencing increased migration.
Prof Carlos Moreno from IAE Paris Sorbonne University emphasizes the need for innovative urban planning to address the challenges and opportunities this growth presents. He envisions ‘proxilience,’ a concept promoting resilience through proximity and accessibility to community facilities.
Optimism at Big 5 Global
At the recent Big 5 Global event in Dubai, industry leaders expressed optimism about the UAE’s demographic potential. Discussions highlighted the importance of integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces to enhance quality of life.
As central areas in Abu Dhabi and Dubai become more crowded, developers are turning to peripheral lands for expansion, similar to suburban growth in North American cities. Areas like Al Ain Road and Dubai South are evolving from city fringes to self-sufficient communities.
Commercial real estate experts, including Jay French and Jack Sellers, predict these areas will become vibrant communities fueled by off-plan purchases, while traditional prime real estate remains valuable.
Building Smarter for the Future
The construction sector faces increased pressure to innovate. Jay French advocates for using steel framing, a sustainable method suitable for modular construction, to meet the demands of rapid urban expansion.
Despite the overall optimism, experts caution that maintaining inclusivity and infrastructure development is crucial for sustaining quality of life in growing urban spaces. Balancing economic progress with community well-being remains a challenge for the UAE’s urban planners.

Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Exploring the Role of Telemedicine in Medical Education
Exploring the Role of Telemedicine in Medical Education
In a recent study published by Frontiers, researchers delved into the transformative impact of a telemedicine-based course on undergraduate medical students during the COVID-19 pandemic. As the pandemic reshaped the landscape of healthcare, telemedicine emerged as a vital tool, not only in patient care but also in medical education.
The Study’s Core Findings
The study, conducted in Indonesia, focused on the reflections of medical students who participated in a telemedicine-based course designed to monitor COVID-19 patients in self-isolation. This innovative approach aimed to bridge the gap created by the suspension of traditional clinical rotations, providing students with crucial learning opportunities despite the pandemic’s constraints.
Four main themes emerged from the students’ self-reflective writings:
- Communication and Empathy: Students learned the importance of clear communication and empathy while interacting with patients remotely. This experience highlighted the challenges of building rapport without face-to-face contact.
- Professional Identity Formation: The course fostered a sense of purpose and responsibility among students, reinforcing their professional identity as future doctors.
- System-Based Practice: Students gained insights into the complexities of healthcare systems and the importance of interprofessional collaboration in pandemic management.
- Patient-Centered Care: The course emphasized the need for holistic, patient-centered care, considering patients’ biopsychosocial backgrounds.
Implications for Medical Education
This study underscores the potential of telemedicine to enhance medical education by providing students with real-world experiences in patient care. By involving students in telemedicine, medical schools can cultivate essential skills such as adaptability, empathy, and communication, which are critical for future healthcare professionals.
The findings also suggest that telemedicine can complement traditional clinical education, offering a valuable alternative in situations where direct patient interaction is limited. As telemedicine continues to play a significant role in healthcare, its integration into medical curricula is likely to persist, preparing students for the evolving demands of modern medical practice.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, the implementation of telemedicine in medical education requires careful planning and adequate resources. Medical schools must ensure that students and clinical supervisors receive proper training and support to maximize the potential of telemedicine-based learning.
Additionally, addressing disparities in access to telemedicine across different regions is crucial to ensure equitable learning opportunities for all students.
Conclusion
The study provides compelling evidence of the benefits of incorporating telemedicine into medical education. By embracing this approach, medical schools can equip students with the skills and experiences needed to navigate the challenges of future healthcare practice, ultimately contributing to the development of competent, patient-centered physicians.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Transformative Role of AI in Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care and Health Management
The Role of AI in Healthcare
AI technology, according to a National Academy of Medicine report, holds the potential to improve clinical outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance population health. In the realm of preventive care, AI is being utilized in radiology to expedite cancer screenings, such as mammograms and lung cancer screenings. For example, at the Mayo Clinic’s PKD Center, AI automates the analysis of kidney images, reducing the process from 45 minutes to mere seconds, thereby aiding in the early detection of polycystic kidney disease.Risk Assessment and AI
AI’s capabilities extend to risk assessment, particularly in cardiology. A study by the Mayo Clinic demonstrated AI’s proficiency in identifying individuals at risk of left ventricular dysfunction, a condition often asymptomatic but potentially fatal. AI models can now alert patients to significant coronary artery calcium levels, predicting heart attack or stroke risks.Advancing Medicine and Public Health
Beyond individual patient care, AI is instrumental in advancing public health. It assists individuals in managing chronic conditions like asthma and diabetes by facilitating timely interventions and reminders. Moreover, AI’s ability to analyze social media trends could have been pivotal in predicting and managing health crises, such as the early stages of COVID-19, as suggested by a study on internet search correlations.AI’s Impact on Patient Care
While some may question AI’s ability to match human healthcare, studies indicate that AI can outperform traditional methods in certain scenarios. For instance, AI has been more accurate than current pathology methods in predicting survival rates for mesothelioma patients and has enhanced the accuracy of colonoscopy procedures by identifying colon polyps.AI and Healthcare Professionals
AI’s role is not to replace healthcare professionals but to augment their capabilities. It can save time by handling tedious tasks, like writing clinical notes and processing vast amounts of medical data. However, human expertise remains crucial for providing clinical context and translating AI findings into actionable insights for patients.Challenges and Future Directions
Despite AI’s promise, challenges remain, including potential biases and the need for effective regulation. AI systems must be trained on diverse datasets to avoid perpetuating existing healthcare disparities. As the Mayo Clinic and other members of the Health AI Partnership emphasize, ensuring equitable and safe AI implementation is essential.As AI continues to evolve, it promises to revolutionize healthcare by improving diagnostics, enhancing remote monitoring, and anticipating disease risks. However, its success hinges on a collaborative approach that leverages both technological advancements and human expertise.

Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Future of Medical Networking
Professional Networking and Collaboration
In today’s interconnected world, medical networking transcends traditional boundaries, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing at a global level. Advanced platforms are connecting healthcare professionals with peers, mentors, and experts worldwide, facilitating rich discussions, advice-seeking, and peer learning. These networks are crucial for enhancing clinical decision-making and keeping professionals abreast of the latest medical advancements.Patient Education and Public Health Awareness
The COVID-19 pandemic has heightened individuals’ awareness of their health choices, leading to increased community-focused health initiatives. Through platforms like social media, healthcare institutions can disseminate valuable advice on preventive care and self-care, reaching a broader audience to foster healthier communities. Public health campaigns play a vital role in spreading crucial messages, such as vaccination drives and mental health awareness, while addressing medical misinformation effectively.Patient Support and Community Building
Medical networking also provides invaluable support through patient advocacy and community-building efforts. These platforms create safe spaces for individuals with similar health conditions to connect, share experiences, and offer mutual support. This fosters a sense of belonging and empowers patients to navigate their journeys confidently. Additionally, dedicated mental health resources are shared within these networks to promote self-care and provide professional guidance.Recruitment and Career Development
For healthcare professionals, medical networking offers numerous opportunities for career advancement and personal branding. From discovering job opportunities to engaging in networking events and accessing continuing education resources, these networks ensure professionals stay aligned with evolving practices. They also support professional branding by allowing individuals to share their expertise and achievements, enhancing their visibility within the industry.Research and Clinical Trial Recruitment
Medical networking plays a critical role in advancing research and clinical trials by connecting healthcare professionals, researchers, and patients. This targeted approach accelerates trial enrollment and enhances research outcomes by reaching specific patient populations. It also facilitates the dissemination of research findings, promoting collaboration and integrating evidence-based practices into clinical care.As highlighted by Dr. Prashant Bhand, Co-founder & Managing Director of LinkOmed, the future of medical networking is deeply intertwined with innovation and integration. With the emergence of AI-enabled solutions and telemedicine, the healthcare landscape is becoming more inclusive and efficient, setting the stage for a sustainable and collaborative patient-centric ecosystem.
For more insights, visit the original article on eHealth Magazine.

Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Innovative Urban Expansion: The UAE’s Vision for Sustainable Living
The concept of the 15-minute city, which aims to provide essential amenities within a short walk or bike ride from residents’ homes, is gaining traction as a model for future urban planning. This approach was a focal point at the recent Big 5 Global event in Dubai, where experts, including Prof Carlos Moreno, emphasized the importance of creating proxilience—resilient communities built on the principle of proximity.

In cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi, where central areas are already densely populated, developers are looking to the outskirts to accommodate new residents. Areas such as Dubai South and Al Ain Road are poised to become self-sufficient communities, echoing the suburban expansion seen in North America’s Sun Belt cities. As Jack Sellers of YallaValue noted, these developments are transforming Dubai into a collection of sub-cities, with an increasing trend towards off-plan property purchases.
Building Smarter for the Future
The pressure on the construction sector to innovate is mounting. Jay French, CEO of Matthews for Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, advocates for the adoption of steel framing and modular construction methods, which offer both speed and sustainability benefits. These techniques could alleviate pressure on existing construction resources and provide a more efficient path forward.
Despite the optimism surrounding these developments, experts caution that rapid urban growth presents challenges. Dr Akram Awad of Boston Consulting Group stresses the need for inclusivity in urban planning, ensuring that all residents feel a sense of belonging. Meanwhile, Dr Anas AlMughairy highlights the critical role of infrastructure in supporting new communities, noting the importance of planning ahead to balance economic growth with quality of life.
As the UAE continues to evolve, these new urban landscapes must navigate the complexities of rapid expansion while striving to create vibrant, livable environments for all.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Call for Climate Change in Medical Curricula
The Call for Climate Change in Medical Curricula
As the world grapples with the multifaceted impacts of climate change, a new urgency is emerging within the medical community. Experts argue that medical curricula must evolve to include comprehensive climate change education, a topic that was recently at the forefront of discussions at the Asia-Pacific forum of the World Health Summit in Melbourne. This forum highlighted the critical need for future health professionals to understand and mitigate the health impacts of global warming, which are becoming increasingly evident across all fields of human health.Escalating Health Crisis Jonathan Patz, a visiting professor at Monash University and a lead author for the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, emphasized the severity of the situation. “Climate crisis is a human health emergency,” he stated, underscoring that climate change exacerbates nearly every type of illness. From waterborne diseases caused by extremes in the water cycle to respiratory issues linked to wildfire smoke, the pathways through which climate change impacts health are numerous and complex.

Education as a Tool for Change Despite the increasing recognition of these issues, a 2020 survey revealed that only 15 percent of medical schools had incorporated the health impacts of climate change into their curricula. This gap in education has prompted calls from experts like Professor Patz and others to expand medical training to prepare future health professionals for the realities of climate-related health challenges. An open letter from 2022 urged educators to ensure graduates can identify, prevent, and respond to these impacts.
Global Health and Policy Implications The forum also highlighted the broader implications of climate change on global health policies. Renzo Guinto of Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore pointed out the mental health challenges associated with climate anxiety, particularly among young people in countries like the Philippines. He advocated for embedding climate health content into health curricula to address these emerging issues and ensure a steady supply of informed health workers.
Opportunities and Challenges While the challenges are significant, there are also opportunities for health benefits as the world tackles the climate crisis. Professor Patz noted that addressing air pollution from fossil fuels, which accounts for over 5 million premature deaths annually according to a BMJ report, could lead to substantial health improvements.
Conclusion
As the forum concluded, the message was clear: integrating climate change education into medical curricula is not just an option but a necessity. This integration will equip future health professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to face one of the most pressing global health emergencies of our time. For more insights from the original article, visit Times Higher Education.Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics: A Revolution in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics: A Revolution in Healthcare
The global market for artificial intelligence in diagnostics is poised for remarkable growth, with projections estimating it to reach USD 7.3 billion by 2032. This surge, as reported by GlobeNewswire on October 7, 2024, is primarily driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the escalating demand for AI-driven diagnostic tools.

Unveiling the Market Dynamics
The artificial intelligence in diagnostics market was valued at USD 1.1 billion in 2023. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.2% anticipated from 2024 to 2032, the market is on a robust development trajectory. The rise in chronic diseases, such as diabetes and cardiovascular conditions, is a significant factor fueling this growth.
Healthcare providers are increasingly turning to AI solutions to enhance early detection, ensure precise diagnoses, and facilitate tailored treatment strategies. These tools are indispensable in managing the high volume of medical data, offering faster and more reliable diagnostic processes, and intensifying the focus on personalized medicine.
Radiology: A Pioneering Segment
In 2023, the radiology segment led the artificial intelligence in diagnostics market with a revenue share of 28.4%. Radiology has been at the forefront of AI adoption, leveraging advanced tools to interpret vast amounts of medical images, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. This early adoption has resulted in mature and refined AI tools, now widely trusted across healthcare facilities.
North America’s Leadership
North America accounted for USD 451.6 million in the artificial intelligence in diagnostics market in 2023. With a projected CAGR of 21.2% from 2024 to 2032, the region stands out as a leader in embracing state-of-the-art healthcare technologies. The high prevalence of chronic diseases and a robust healthcare infrastructure further bolster the demand for AI-based diagnostics.
Key Players and Future Prospects
Major players in the market include Aidoc, AliveCor Inc., Digital Diagnostics, Inc., Enlitic, IBM Corporation, and Siemens Healthineers, among others. As the industry continues to evolve, swift advancements in AI technologies and the widespread adoption of digital healthcare platforms are expected to hasten the integration of AI tools across various diagnostic applications.
For more insights, the full report and additional resources can be accessed through the following links: Request a Sample, Report Customization, and Browse More Reports.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Revolutionizing Medical Education with Extended Reality
Revolutionizing Medical Education with Extended Reality
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical education, a new player has emerged, promising to revolutionize the way future doctors are trained. The integration of eXtended Reality (XR) technologies, which encompass both Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), is reshaping the educational landscape by addressing the limitations of traditional methods.
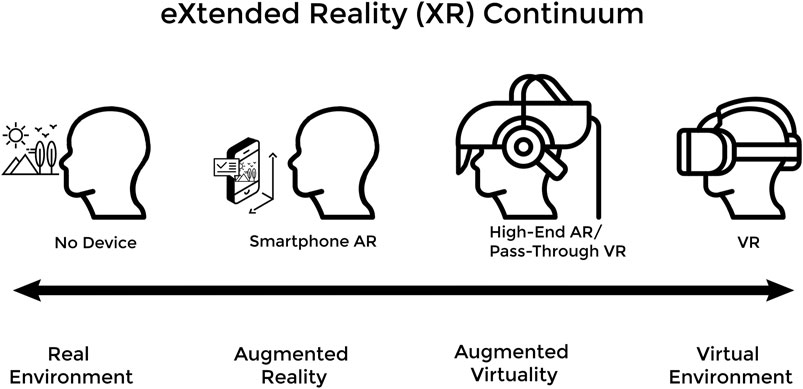
Transforming Learning Experiences
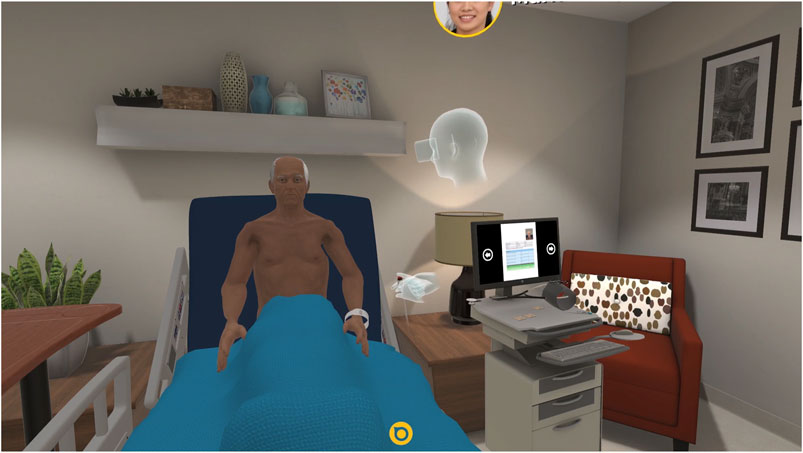
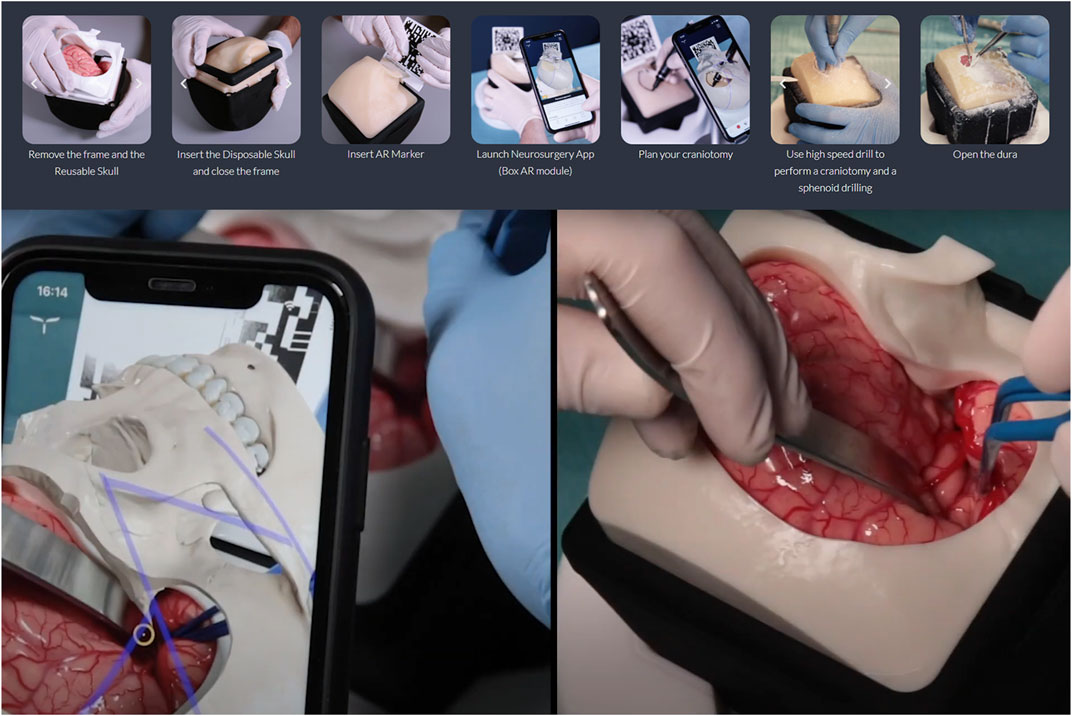
XR technologies are bridging gaps in medical training by offering immersive learning experiences that enhance the understanding of complex 3D structures, improve empathetic communication skills, and refine surgical techniques. Traditional educational tools like cadavers and patient actors are often costly and limited in availability. XR offers a cost-effective alternative, allowing students to practice repeatedly in a safe, controlled environment.
Adapting to a Post-Pandemic World
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of virtual learning tools. Medical institutions that had invested in XR technologies found themselves better equipped to adapt to remote learning environments. This shift not only ensured continuity in education but also highlighted the potential of XR in providing accessible and engaging learning experiences outside traditional classrooms.
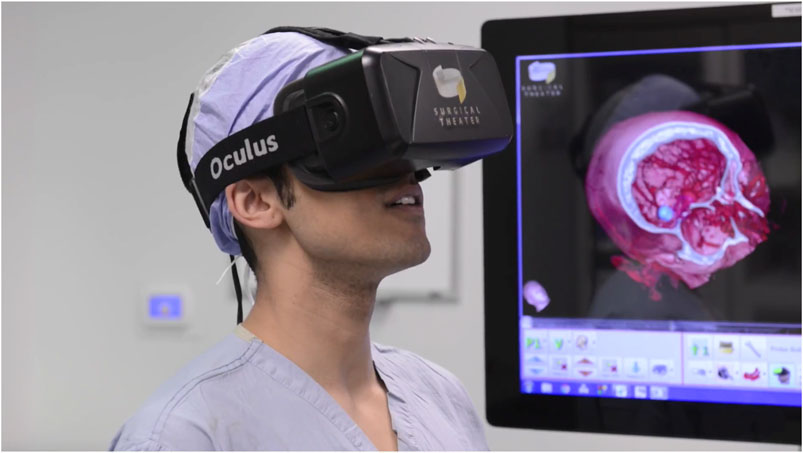
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its promise, the widespread adoption of XR in medical education faces challenges. Issues such as cybersickness, faculty resistance, and the need for robust evidence of educational superiority remain. However, as XR technology and its applications continue to evolve, these hurdles are expected to diminish. The future of medical education is poised to embrace these advancements, fostering a new generation of healthcare professionals equipped with cutting-edge skills.
Conclusion
As XR technologies continue to advance, their integration into medical education is not just a possibility but a necessity. By embracing these tools, medical schools can provide students with a more immersive, engaging, and effective learning experience, preparing them for the challenges of modern healthcare.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Genetic Testing: A New Dawn in Healthcare
Genetic Testing: A New Dawn in Healthcare
In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare, genetic testing is emerging as a pivotal force, promising to transform patient care through precision medicine. The insights derived from our genetic codes hold the potential to not only prevent diseases but also optimize treatments and promote healthier living. Yet, as highlighted in a recent MedCity News article, the journey towards realizing this potential is fraught with challenges, particularly around patient privacy and data sharing.
The Role of Information Technology
A critical component in addressing these challenges is information technology security. Organizations are turning to certifications like HITRUST to establish standards for safeguarding sensitive information. By aligning with these standards, they can protect data while facilitating the sharing necessary to enhance medical knowledge and patient care.
Collaborative Efforts and Data Sharing
Collaboration is at the heart of advancing genetic testing. Companies are contributing de-identified variant data to public health databases such as ClinVAR and the SEER Cancer Registries. These efforts, supported by cancer research registries, deepen insights and expedite advancements in patient care.
The analysis of expansive data sets is crucial for understanding diseases, allowing researchers to access, assess, and test hypotheses. This collaborative approach is paving the way for tailored treatment plans and new biological discoveries, enhancing early disease detection and intervention.
Integration with Electronic Health Records
Integrating genetic testing with Electronic Health Records (EHR) is another key strategy for improving patient outcomes. Collaborations with EHR vendors like Epic, Flatiron, and Athena streamline processes, making it easier for providers to order genetic products, optimize screening protocols, and identify potential pharmacogenetic interactions. Such collaborations break down silos, enhancing data exchange for more effective research and patient care.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite the promising progress, the integration of genetic testing into mainstream medicine presents challenges, including managing the vast volume of genomic data. Companies are focusing on presenting complex clinical interpretations, integrating common data ontologies, overcoming data fragmentation, and ensuring data privacy to address these hurdles.
Looking ahead, the industry anticipates significant advancements, with trends like developing tests for early cancer recurrence detection and embracing a multi-omics approach that integrates RNA, proteins, and AI insights. The integration of generative AI for documentation and genetic counseling is another notable development on the horizon.
A New Era in Healthcare
Genetic testing represents more than just a scientific advancement; it signifies a fundamental shift in how we approach health and wellness. As public understanding grows and technology advances, we find ourselves at the dawn of a new era in healthcare, where our genetic code becomes a roadmap to better health and longevity.

About the Author
Kevin Haas, Ph.D., serves as the Chief Technology Officer at Myriad Genetics, where he leads the development of the precision medicine platform. With expertise in molecular simulation and machine learning, Haas is advancing genomics and digital patient/provider experiences. He has co-authored 16 peer-reviewed publications and nine patent applications, bringing a wealth of experience to his role.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Sustainable Architecture: Blending Innovation with Ecological Responsibility
Global Inspirations in Sustainable Architecture
From the towering Quay Quarter Tower in Sydney to the serene March House along the River Thames, these projects exemplify sustainable architecture’s potential to redefine urban landscapes. The eco-friendly synagogue in Palo Alto and the Black & White Building in London showcase how traditional and contemporary designs can coexist harmoniously, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Principles of Sustainability
Sustainable architecture is not just about aesthetics; it’s a commitment to the environment. Key principles include using locally sourced materials, minimizing energy consumption, and ensuring the longevity and adaptability of structures. The 2022 Obel Prize-winning carbon-neutral composite cement by Seratech is a testament to the innovative materials that are shaping the future of construction.
Innovative Projects
Projects like the Slot House in Utah and the Reference Center of Babassu Coconut Breakers in Brazil highlight the diverse applications of sustainable architecture. These buildings are designed to support local communities and reduce environmental footprints, embodying the ethos of sustainability.
- Kempegowda International Airport Terminal 2 in India, a marvel of green technology and design.
- The Magasin Électrique in France, using sustainable materials and innovative reuse.
- Citizens House in London, supporting community through affordable housing.
Future-Proofing Our World
The journey toward sustainable architecture is ongoing, with each project serving as a beacon of what’s achievable when creativity meets ecological awareness. As we look to the future, these structures remind us that architecture can be both a shelter and a steward of the environment.

Conclusion
The original article from Wallpaper.com offers an in-depth exploration of these remarkable endeavors, highlighting the transformative power of sustainable architecture. It is a call to action for architects, designers, and communities to embrace sustainability as a core principle in building a better future.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
AI in Clinical and Molecular Diagnostics: A Market on the Rise
AI in Clinical and Molecular Diagnostics: A Market on the Rise
In a significant development, the AI in Clinical and Molecular Diagnostics Market is set to experience remarkable growth, projected to surge from USD 2.6 billion in 2024 to USD 8.9 billion by 2029. This growth is driven by the integration of advanced AI technologies such as machine learning and deep learning into traditional diagnostic methodologies like imaging, genomics, and laboratory testing.
Personalized Medicine and AI Integration A growing emphasis on personalized medicine and the integration of AI into healthcare systems are key factors propelling this market expansion. The demand for accurate and efficient diagnostic solutions is rising, as AI technologies enhance the capabilities of traditional methods.
Regional Focus and Industry Initiatives Countries in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are leading the charge with digital health initiatives, fostering innovative diagnostic solutions. Major industry players are investing in research and development, forming strategic partnerships, and expanding their product portfolios to leverage emerging opportunities in developing markets.
Comprehensive Market Analysis The report provides a detailed analysis of market size, growth trends, and segmentation by technology and application. It examines the challenges and opportunities influencing AI adoption in clinical and molecular diagnostics, focusing on specific applications in imaging, genomics, and laboratory diagnostics. Notable companies featured in the report include Siemens Healthineers AG, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Koninklijke Philips N.V., and Fujifilm Holdings Corp.
Emerging Trends and Opportunities Emerging trends, such as AI integration in personalized medicine and telehealth, present significant opportunities for stakeholders including healthcare providers, technology developers, and policymakers. The report serves as an essential reference for those aiming to navigate and capitalize on the evolving AI landscape in diagnostics.
For more comprehensive insights, visit the ResearchAndMarkets.com report.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
AI: A Revolution in Healthcare’s Future
The Promise of AI in Healthcare
AI is not a distant dream but a present reality, already integrated into everyday life through virtual assistants like Alexa and Siri. However, its potential extends far beyond convenience, reaching into the intricate world of healthcare. According to the National Academy of Medicine, AI can significantly enhance patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and improve population health.In radiology, for instance, AI accelerates cancer screening results, offering swift and accurate diagnoses. A notable application is in the analysis of polycystic kidney disease (PKD), where AI rapidly evaluates total kidney volume, a critical factor in predicting disease progression.
Cardiology and Risk Assessment
AI’s capabilities extend into cardiology, where it has demonstrated a remarkable ability to identify risks for conditions like left ventricular dysfunction before symptoms appear. This proactive approach allows for early intervention, potentially averting serious health crises. AI tools also detect coronary artery calcium, signaling the risk of heart attacks or strokes years in advance, thus offering a window of opportunity for preventive care.Beyond Diagnostics: AI in Public Health
AI’s influence is not confined to individual patient care. It plays a vital role in public health management, particularly in disease prevention and outbreak prediction. During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI could have analyzed internet search trends and social media data to anticipate outbreak hotspots, aiding public health officials in making informed decisions to curb the spread.AI as a Complement to Human Expertise
While AI shows promise in enhancing medical accuracy, such as in predicting mesothelioma survival and improving colonoscopy accuracy, it is not intended to replace healthcare professionals. Instead, AI serves as an invaluable assistant, managing routine tasks and sifting through vast volumes of medical literature, thus freeing doctors to focus on patient care.However, the integration of AI in healthcare is not without challenges. Concerns about bias in AI algorithms, if trained on non-representative data, and the dissemination of misinformation through AI chatbots underscore the need for effective regulation.
The Road Ahead
The future of AI in healthcare is bright, with exciting possibilities on the horizon. From remote health monitoring and early diagnosis of imperceptible conditions to selecting suitable clinical trials, AI stands to redefine the landscape of medical care. The Mayo Clinic is at the forefront of this innovation, striving to harness AI’s potential to create new methods for diagnosing, treating, predicting, preventing, and curing diseases.
As AI continues to evolve, its role in healthcare will undoubtedly expand, offering new tools and insights that promise to enhance both individual and public health outcomes.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Building an Integrated Approach to Real Estate Sustainability
In a revealing examination of the real estate sector’s sustainability efforts, a recent Deloitte report sheds light on the pressing challenges and strategic pathways for achieving environmental compliance. The report, titled “Building an Integrated Approach to Real Estate Sustainability,” highlights that nearly 60% of global real estate CFOs lack the necessary data, processes, or internal controls to comply with current environmental regulations.

To bridge this gap, Deloitte suggests that real estate firms must foster cross-departmental collaboration. Key stakeholders, including finance leaders, sustainability officers, engineers, and tax experts, should work in unison to align their strategies with both financial and sustainability goals. This integrated approach is vital for navigating the complex landscape of tax incentives and regulatory challenges, which are critical for achieving sustainability objectives.
Key Areas for Integration
- Tax and Regulatory Opportunities: The report emphasizes the importance of identifying incentives and addressing challenges. However, only 32% of firms plan to leverage tax-saving opportunities, indicating a significant area for growth.
- Risk and Financial Modeling: Prioritizing physical and transition risks is crucial for compliance and investment security. Conducting risk assessments can enhance understanding and strategy integration.
- Accounting and Reporting: With new regulations like the SEC climate rule, aligning sustainability with financial reporting is becoming increasingly essential.
- Strategy and Energy Sourcing: A focus on renewable energy sources is paramount, with companies like Slate Asset Management making substantial investments.
- Technology Integration: The adoption of smart technologies, such as IoT devices, is critical for monitoring consumption. Digital twins can optimize operations and streamline reporting.
The Deloitte report also underscores the need for real estate firms to align their energy sourcing strategies with tax incentives to enhance ROI while meeting sustainability targets. This alignment requires collaboration across various stakeholders, from IT and finance to developers and engineers, to build a robust infrastructure capable of supporting sustainability goals.
Looking Ahead
As environmental standards continue to evolve, the future of real estate sustainability will likely be shaped by regulatory changes, market expectations, and technological advancements. Real estate companies are urged to integrate sustainability into their core operations, leveraging industry-specific solutions to navigate complexities and maintain a competitive edge.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Blockchain Revolution: Building the Future of Finance with DeFi
By embracing DeFi and the blockchain revolution, individuals can seize control of their financial futures. This new paradigm opens doors to innovative investment opportunities and fosters a more inclusive global economy. As highlighted in the original article from the London Daily News, the impact of DeFi is monumental, reshaping the very fabric of the financial world.
Understanding Blockchain Technology in Finance
Blockchain technology is at the heart of this transformation, providing a decentralized, secure, and transparent framework for transactions. Unlike traditional systems, blockchain’s distributed ledger records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring no single entity has control. This decentralization enhances security and fosters trust, as altering any entry requires consensus.
- Enhances security through cryptography, minimizing fraud risk
- Increases transparency, allowing real-time transaction verification
- Reduces costs by eliminating intermediaries
- Facilitates faster transactions for near-instant cross-border payments
The Purpose of DeFi Applications
In this new financial ecosystem, DeFi leverages blockchain technology to offer decentralized financial services. DeFi promotes a peer-to-peer (P2P) approach, eliminating the need for traditional gatekeepers. Services such as lending, borrowing, and investing become more transparent and user-controlled, as explored in the future of blockchain in finance.
How Does DeFi Work?
DeFi’s foundation in blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum, enables decentralization. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts, automate financial processes, removing the need for intermediaries and promoting accessibility, security, and transparency.
Reshaping the Future of Finance
The transformative power of DeFi lies in its ability to address the challenges of conventional financial systems. By minimizing the need for traditional intermediaries, DeFi streamlines transactions, reducing costs and enhancing efficiency. Platforms like Aave exemplify this by allowing borrowers to connect directly with lenders, bypassing banks.
Greater Accessibility
Smart Contracts Automation
Increase Security
New Financial Products
Programmable Money

Global Financial Inclusion
DeFi’s potential for global financial inclusion is immense, offering services to underbanked populations worldwide. By eliminating intermediaries and leveraging smartphones, people in rural areas gain access to financial opportunities previously unavailable.
As we navigate this blockchain revolution, investing in DeFi solutions becomes not only feasible but essential. Embracing DeFi unlocks unprecedented opportunities, reshaping the future of finance.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Artificial Intelligence: A New Frontier in Neurological Care
Artificial Intelligence: A New Frontier in Neurological Care
In a rapidly evolving medical landscape, artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a game-changer in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological emergencies. A recent comprehensive review published in Frontiers highlights the transformative potential of AI in neurology, particularly in acute scenarios like stroke and traumatic brain injury.Revolutionizing Diagnosis and Treatment
AI’s integration into neurology is not just a fleeting trend; it’s a significant shift in how healthcare professionals approach complex neurological disorders. Leveraging machine learning algorithms and deep learning models, AI systems can analyze vast datasets with unprecedented speed and accuracy. This capability is crucial in time-sensitive situations where every second counts, such as identifying candidates for thrombolytic therapy in stroke cases.
According to Lee et al. (2020), machine learning has already demonstrated its prowess in identifying strokes within a critical 4.5-hour window. Such advancements underscore AI’s potential to enhance patient outcomes by facilitating rapid decision-making.
AI in Neurological Imaging
The role of AI in diagnostic imaging is particularly noteworthy. Deep learning models, as discussed by Litjens et al. (2017), have been trained to interpret complex medical images, often outperforming human experts. This technology is pivotal in detecting early signs of neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, as evidenced by Ardila et al. (2019).
Ethical and Practical Challenges
Despite its promise, the deployment of AI in healthcare is not without challenges. Ethical concerns, such as data privacy and algorithmic bias, must be addressed to ensure equitable patient care. The “black box” nature of AI systems often leaves clinicians and patients questioning the transparency of AI-driven decisions. As AI continues to integrate into healthcare, it is imperative to establish robust ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks.
Furthermore, the practical implementation of AI in clinical settings requires significant investment in infrastructure and training. As highlighted by Shickel et al. (2018), predictive analytics in healthcare can revolutionize patient management, but only if healthcare providers are equipped to harness these technologies effectively.
Looking Ahead: Future Directions
The future of AI in neurology is bright, with emerging trends pointing towards more personalized and precise treatment strategies. The integration of AI with wearable devices and telemedicine platforms promises continuous monitoring and early intervention for chronic neurological conditions.
However, to fully realize AI’s potential, ongoing research and development are essential. Future studies should focus on creating more interpretable AI models and exploring their long-term efficacy in diverse healthcare settings.
In conclusion, AI is poised to redefine neurological care, offering new hope for patients and clinicians alike. As the field advances, it is crucial to balance innovation with responsibility, ensuring that AI technologies are deployed ethically and equitably across the healthcare spectrum.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Celebrating Commitment to Physician Well-being
Celebrating Commitment to Physician Well-being
In a significant move to combat physician burnout, the American Medical Association (AMA) has recognized 62 health care organizations through its Joy in Medicine™ Health System Recognition Program. These organizations, representing over 140,000 physicians, have been acknowledged for their innovative strategies aimed at reducing stress and enhancing mental health among doctors. This recognition underscores a broader commitment to fostering environments where physicians can thrive and rediscover the joy in their profession.
AMA President Bruce A. Scott, MD, emphasized the importance of addressing systemic issues rather than placing the burden of change on physicians themselves. He noted the growing national movement to transform healthcare work systems to tackle the root causes of physician burnout.
The recognized organizations join a distinguished cohort of 72 health systems from 2023, collectively representing over 230,000 physicians. This year’s honorees have set a high standard by prioritizing commitment, leadership, teamwork, and practice-environment efficiency.
Decline in Burnout Rates
Significantly, physician burnout rates have dropped below 50% for the first time since 2020. This decline highlights the effectiveness of ongoing efforts and the crucial role of programs like the Joy in Medicine™ Health System Recognition Program.Recognition Levels
The program offers three levels of recognition: Bronze, Silver, and Gold. This year, El Rio Health achieved Gold status, while 12 health systems earned Silver recognition, including Bayhealth and Dayton Children’s Hospital.Continued Advocacy and Support
The AMA remains at the forefront of advocacy for physician well-being, removing administrative burdens and providing real-world solutions. As Christine Sinsky, MD, AMA vice president of professional satisfaction, stated, “Reducing burnout requires health system leaders to invest in systems-based solutions that provide resources to match the demands placed on physicians.”For more details on recognized organizations and the program, visit the official AMA page.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Global Hospital Services Market Set for Substantial Growth
Global Hospital Services Market Set for Substantial Growth
The global hospital services market is undergoing a significant transformation, with projections indicating robust growth over the next decade. As of 2023, the market was valued at USD 13.1 trillion and is expected to soar to an impressive USD 24.1 trillion by 2033, boasting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3%. This optimistic forecast, reported by Market.us Media, is driven by advancements in medical technology, increased healthcare expenditures, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases.Conclusion
In conclusion, the hospital services market is poised for robust growth, with advancements in technology and an increasing need for specialized healthcare services playing pivotal roles. While there are challenges to navigate, the overall market trajectory is positive, with North America expected to maintain its leading position in the coming years.Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Unlocking the Potential of Modular Construction in Ontario’s Housing Market
In the bustling realm of Ontario’s housing market, modular construction is emerging as a beacon of hope amid a pressing demand for new homes. However, as Albert Bendersky, vice-president of design at Hamilton’s BECC Modular Solutions, points out, several barriers must be dismantled to fully harness this innovative construction method.
Chief among these obstacles is the absence of formal pre-approval or recognition by provincial and municipal authorities for standardized modular units. The existing building code, described as inflexible, does not yet accommodate the revolutionary technologies that modular construction could bring to the fore.
In an effort to bridge these understanding gaps, BECC recently hosted a group of planners at its facility, coinciding with the annual Ontario Professional Planners Institute conference. During this event, Bendersky emphasized the potential of modular construction to meet various municipal and aesthetic requirements, stating, “We can achieve the same results that have been achieved before,” advocating for a shift towards new technological solutions in the sector.
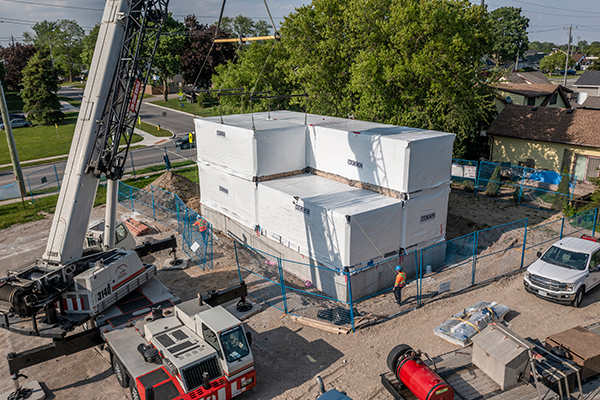

The essence of resolving the housing crisis, Bendersky asserts, lies in the mass-production of high-quality buildings. This involves integrating 21st-century industrial technologies akin to those used in automobile and electronics manufacturing. BECC, for instance, leverages Hamilton’s high-grade steel as a key component in their process, although other materials like wood or concrete are also viable.
The manufacturing process at BECC begins with pre-cut and pre-drilled steel parts, assembling modules complete with wiring, piping, insulation, and more. This modular approach aims to significantly reduce time and costs, paralleling modern industrial efficiency.
Bendersky highlighted a current project for a California client to illustrate the efficiency of modular construction when supported by an effective approvals system. Unlike Ontario’s layered planning and political processes, California’s system allows for streamlined approvals, enabling projects to proceed without repetitive bureaucratic hurdles.
To truly enhance the adoption of modular construction in Ontario, Bendersky suggests the development of a pre-approval system by large municipalities. Such a system would expedite projects by alleviating some of the red tape associated with building permits, especially for small to mid-size developments.
The integration of new technologies into the building code is essential, as existing codes hinder progress by not recognizing the capabilities of modern construction methods, Bendersky explained.
In conclusion, BECC is on the cusp of further technological advancement with plans to introduce robotic systems, poised to enhance manufacturing speed and efficiency. As the industry becomes more sophisticated, sustainable construction standards like Passive Haus and net-zero should become achievable goals, mirroring traditional building achievements.
Despite these challenges, the sector is advancing rapidly with the help of Building Information Modelling (BIM) platforms and AI tools, enabling a more scientific approach to construction. Follow Don Wall on X/Twitter for ongoing updates in this rapidly evolving field.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
The Future of Personalized Medicine: Bridging the Gap in Health Disparities

The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) reports that while breast cancer mortality has decreased, Black women still face a 40% higher death rate compared to their White counterparts. This inequity is partly due to the fact that Black women are less frequently offered genetic screenings that could potentially save their lives.
Bridging the Gap
Efforts to rectify these disparities are underway. Initiatives like the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative’s Accelerate Precision Health program aim to expand research at historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs). These programs focus on increasing the representation of diverse genetic profiles in medical research.Moreover, the NIH’s All of Us research program is building one of the largest and most diverse health databases in the world. This initiative seeks to understand how various factors such as environment and socioeconomic status influence health, with the ultimate goal of making precision medicine accessible to all communities.
Challenges and Responsibilities
Despite these promising efforts, systemic barriers remain. The lack of diverse representation in genetic studies, high costs of genetic testing, and limited outreach to marginalized communities hinder the equitable distribution of personalized medicine’s benefits. As the field continues to evolve, the urgency to address these challenges grows.Rick Kittles, PhD, of Morehouse School of Medicine, emphasizes that academic medical centers must commit to resolving inequities within their communities. This includes fostering trust and building relationships with underrepresented groups to ensure that the advancements in personalized medicine are inclusive and beneficial to all.
As personalized medicine continues to develop, the question remains: will it be a beacon of hope for all, or a gateway to new health disparities?
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Discover more from Cameron Academy
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

































