Hitting Home: Housing Affordability Crisis in the U.S.
Hitting Home: Housing Affordability in the U.S.
The American housing market is grappling with a crisis of affordability that is reshaping the landscape of homeownership and renting. A recent analysis by Econofact highlights the growing burden of housing costs on American households. With median house prices now six times the median income—up from four to five times two decades ago—the dream of homeownership is slipping away for many. Even renters, who have historically found refuge in more affordable options, are feeling the pinch as the ratio of median rents to median income has crept from 25% to 30%.
The Facts Behind the Crisis
- Worsening Affordability: The affordability crisis is not confined to coastal cities like San Francisco and New York. It is a nationwide issue, affecting both urban and rural areas.
- Cost-Burdened Households: A significant increase in cost-burdened renters—those spending more than 30% of their income on housing—has been observed, particularly among those earning between $35,000 and $49,000 annually.
- Geographic Variations: Traditionally affordable regions are seeing rapid price appreciation, shrinking the affordability gap with historically expensive areas.
The issue of housing affordability is compounded by a mix of demographic shifts and regulatory hurdles. The aging population, with more seniors opting to age in place, has contributed to a supply crunch. Meanwhile, zoning laws and other regulatory restrictions limit housing density, exacerbating the shortage. These factors, coupled with the rise in mortgage rates from 3.5% to nearly 8% since early 2022, have made the path to homeownership even steeper.
Hope on the Horizon?
Despite the grim outlook, there are glimmers of hope. The anticipated reversal of the Federal Reserve’s tightening cycle could lower mortgage rates, easing the financial strain on households. Additionally, there are signs of change in urban zoning laws to allow more affordable housing construction. A surge in multifamily housing starts and a large pipeline of apartments under construction may help relieve pressure on rents.The complexity of the housing affordability crisis suggests there is no quick fix. However, with concerted efforts to increase supply and reform regulatory practices, there is potential for a more balanced and accessible housing market. “`
More Articles
Getting licensed or staying ahead in your career can be a journey—but it doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Grab your favorite coffee or tea, take a moment to relax, and browse through our articles. Whether you’re just starting out or renewing your expertise, we’ve got tips, insights, and advice to keep you moving forward. Here’s to your success—one sip and one step at a time!
Revolutionizing Healthcare: NHS Trials AI Tool for Early Diabetes Detection
Revolutionizing Healthcare: NHS Trials AI Tool for Early Diabetes Detection
In an unprecedented leap for preventive medicine, the National Health Service (NHS) in England is poised to trial Aire-DM, a groundbreaking AI tool designed to predict the risk of type 2 diabetes a remarkable 13 years before its onset. This ambitious trial is set to commence in 2025 at both Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust and Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, marking a significant stride in healthcare innovation.
How Aire-DM Works
Aire-DM utilizes advanced AI algorithms to scrutinize electrocardiogram (ECG) readings obtained during routine heart scans. By detecting subtle changes in the heart’s electrical signals—often invisible to the human eye—this technology provides an early warning system for potential type 2 diabetes development. These changes, such as prolonged electrical activation times, are crucial indicators of how diabetes can affect cardiac structure and function. Dr. Libor Pastika, a clinical research training fellow at Imperial College, underscores the transformative potential of Aire-DM, stating, “AI holds enormous potential to transform care, leading to substantial health improvements. By unlocking insights hidden within ECG data, Aire-DM could revolutionize how we predict and manage the future risk of type 2 diabetes.”Importance of Early Detection
Type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions globally, can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and neuropathy. Early detection allows healthcare providers to implement preventive measures, including dietary changes, increased physical activity, and medication, to delay or even prevent the disease’s onset. Traditional methods of identifying diabetes risk often rely on family history, blood sugar levels, and lifestyle factors. However, Aire-DM’s ability to analyze ECG data offers a more precise and proactive approach.
Traditional methods of identifying diabetes risk often rely on family history, blood sugar levels, and lifestyle factors. However, Aire-DM’s ability to analyze ECG data offers a more precise and proactive approach.
Global Implications and Future Prospects
As the first healthcare system globally to implement trials for this AI-based tool, the NHS aims to assess its accuracy, feasibility, and impact on patient outcomes. If successful, Aire-DM could become a standard screening tool in hospitals and clinics worldwide, setting a precedent for future AI applications in medicine. Its success could spur advancements in predicting other chronic conditions, reimagining the future of preventive care. The trial of Aire-DM by the NHS signifies a monumental leap forward in preventive medicine. By leveraging AI to detect diabetes risk early, healthcare providers can intervene sooner, ultimately saving lives and reducing the long-term impact of the disease. As the trial unfolds, it holds the promise of setting a global precedent for integrating AI into routine healthcare, revolutionizing how chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes are managed and prevented. “`Revolutionizing Skin Cancer Diagnosis with AI: Efficacy and Future Prospects
AI’s Role in Revolutionizing Skin Cancer Diagnosis
In a groundbreaking study published by Nature on May 14, 2024, researchers have delved into the burgeoning field of artificial intelligence (AI) in dermatology. The systematic review and meta-analysis focus on AI’s efficacy compared to human clinicians in diagnosing skin cancer, a disease that remains the most common neoplasm worldwide.
AI vs. Clinicians: A Comparative Analysis
The study highlights a comprehensive comparison between AI algorithms and human clinicians, including experienced dermatologists and general practitioners. It reveals that AI can match or even surpass specialists in accuracy, particularly in categorizing skin lesions as benign or malignant. This finding underscores AI’s potential to transform dermatological practices by enhancing diagnostic precision.
Augmented Intelligence in Medical Practices
One of the study’s pivotal insights is the concept of ‘augmented intelligence,’ where AI is integrated into medical practices to assist clinicians. This approach is especially beneficial for generalists and non-specialist clinicians, bolstering their diagnostic capabilities. The study suggests that AI’s collaboration with human expertise can lead to improved diagnostic outcomes, particularly in primary care settings.
Broader Trends in Healthcare
The increasing use of AI in dermatology mirrors a broader trend of incorporating advanced technologies in healthcare to enhance diagnostic accuracy. The structured research approach, using systematic reviews and meta-analyses, consolidates evidence from various studies, providing a quantitative assessment of AI’s capabilities in clinical scenarios.
References and Further Reading
For those interested in further exploring the topic, the original article references key studies such as Lakhani et al.’s work on skin cancer screening, Wu et al.’s systematic review on deep learning in skin cancer classification, and Jones et al.’s review of AI and machine learning algorithms for early skin cancer detection. These studies are accessible through their respective publications:
- Lakhani, N. A. et al. (2014)
- Wu, Y. et al. (2022)
- Jones, O. T. et al. (2022)
- Sangers, T. E. et al. (2023)
Conclusion
This study marks a significant step towards embracing AI in clinical settings, with the potential to revolutionize how skin cancer is diagnosed and managed. It calls for further real-world studies and randomized clinical trials to fully realize AI’s benefits in healthcare.
The Dawn of Personalized Medicine: AI’s Transformative Role in Healthcare
The Dawn of Personalized Medicine: AI’s Transformative Role in Healthcare

In a world where the promise of personalized medicine is finally being realized, Erez Meltzer, CEO & Board Member of Nanox, stands at the forefront of this revolution. With over 35 years of experience leading global companies, Meltzer is witnessing firsthand how artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping patient care, moving beyond mere incremental improvements to offer truly individualized healthcare at scale.
While the concept of personalized medicine is not new, its effective implementation has been hampered by the complexity of human biology and the sheer volume of data involved. Here, AI emerges as a game-changer, providing the computational power and analytical prowess needed to process this complexity and extract actionable insights. As AI continues to learn from the vast amounts of healthcare data, its accuracy and predictive capabilities grow exponentially, enhancing its ability to personalize care.
Revolutionizing Diagnostics and Early Detection
AI is making significant strides in diagnostics and early detection. Advanced algorithms, particularly deep learning models, are analyzing medical imaging data with unprecedented accuracy and speed. These AI systems augment, rather than replace, radiologists, enabling more precise and efficient diagnoses and the ability to quickly identify incidental findings in scans.
The true power of AI in diagnostics lies in its ability to personalize the process. By considering individual risk factors, AI can tailor screening schedules, ensuring high-risk patients receive more frequent screenings while reducing unnecessary procedures for low-risk individuals. This approach not only improves patient outcomes but also optimizes healthcare resources.
Predictive Analytics: A New Frontier in Preventive Care
The potential of AI in predictive analytics is vast. By integrating data from various sources—including electronic health records, genetic information, and lifestyle data—AI models can predict individual patient risks with unprecedented accuracy. For instance, researchers at the University of Virginia have developed an AI model for predicting outcomes in heart failure patients, enabling healthcare providers to tailor their interventions accordingly.
Moreover, models like the pancreatic cancer risk model from MIT’s Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Laboratory have the potential to expand early screening benefits from 10% to 35% of patients. By identifying individual risk factors early, we can develop personalized strategies to manage these risks, potentially reducing the burden of chronic diseases and improving overall health outcomes.
Personalizing Treatment Plans
AI’s impact extends well into the treatment phase. AI-assisted treatment planning is emerging as a powerful tool for clinicians, allowing for more personalized and effective care strategies. A team at Northwestern University’s McGaw Medical Center is creating a model to predict long-term outcomes for breast cancer patients, aiming to recategorize patients for shorter, less intense treatment plans with fewer side effects.
Addressing Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite AI’s massive potential in healthcare, key challenges remain. Integrating AI requires buy-in from various stakeholders, from overloaded IT departments to hesitant doctors. Furthermore, the risk of bias in AI models, if not trained on diverse datasets, can exacerbate existing healthcare disparities. Ensuring fairness and equity in AI-driven healthcare is both an ethical and practical necessity.
As we increasingly rely on AI for healthcare decisions, addressing these challenges is paramount. Ensuring the integrity and adaptability of AI algorithms, mitigating biases, and preserving the human element in healthcare remain essential priorities.
The Path Forward
Looking ahead, AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by enabling personalization across the entire patient journey. However, AI should support, not replace, healthcare professionals. As we continue to develop AI technologies, we must do so responsibly, focusing on improving patient outcomes and maintaining trust. By embracing these technologies ethically, we can create a healthcare system that truly centers on the individual patient.
The AI revolution in healthcare is well underway, and as industry leaders, it is our responsibility to guide this transformation. The potential benefits—lives improved and saved—are too significant to ignore.
DeFi: Revolutionizing the Financial Landscape
DeFi: Revolutionizing the Financial Landscape
In a compelling exploration of the financial landscape, Himanshu Kumar, CEO of AMBCrypto, delves into the transformative potential of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and its implications for traditional banking. Highlighting DeFi’s revolutionary approach, Kumar discusses how the democratization of financial services through blockchain technology is reshaping access, breaking down barriers, and challenging established institutions.DeFi allows for peer-to-peer transactions by removing intermediaries, facilitated by smart contracts that automate agreements without requiring a third party. This not only enhances efficiency but also reduces costs, ultimately making financial services more accessible to a broader audience. The impact on financial inclusion is significant, providing 1.7 billion unbanked individuals with services via a smartphone and internet connection, thus spurring economic growth and empowerment.
Transparency and Trust
Transparency, a core feature of DeFi, is achieved through every transaction being recorded on a public ledger. This transparency builds trust among users by allowing them to verify transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and corruption, and holding platforms accountable.Despite these advancements, challenges remain, particularly in the realm of regulation and security. Kumar stresses the importance of working with regulators to create clear guidelines that protect consumers while allowing innovation to thrive. He also emphasizes the necessity for stringent security measures to foster user confidence in DeFi platforms.
Adapting to Change
The article further discusses the potential for traditional banks to adapt by collaborating with DeFi platforms, which could lead to the development of innovative products and services. It touches upon the need for simplifying user interfaces and educating the public to encourage wider adoption of DeFi.Finally, environmental considerations are acknowledged, calling for a shift towards energy-efficient solutions within the blockchain realm to ensure sustainable growth. Under Kumar’s leadership, AMBCrypto aims to bridge the gap between technology and the public, empowering readers with accurate news and insightful analysis.
In summary, DeFi is not just a trend but a transformative force impacting the future of finance. As Himanshu Kumar aptly states, it opens doors to a more inclusive and transparent financial world.
Revolutionizing Healthcare: Telemedicine Services in 2024
Revolutionizing Healthcare: Telemedicine Services in 2024
As the landscape of healthcare continues to transform, telemedicine has emerged as a pivotal solution for those seeking medical guidance and prescription services from the comfort of their homes. In 2024, telemedicine services have expanded not only in availability but also in the variety of offerings tailored to meet diverse patient needs and preferences. In a recent CNET article, a comprehensive guide was provided on the best telemedicine services, helping individuals select the most suitable option for their healthcare needs.
Sesame Care: Affordable and Transparent
Sesame Care offers a straightforward approach to primary care, mental health consultations, and prescription refills, all while maintaining transparency in pricing. Although it operates out of network with insurance companies, its services remain relatively affordable, making healthcare accessible for budget-conscious individuals.
HealthTap: Continuity in Care
HealthTap distinguishes itself by fostering a strong doctor-patient relationship, allowing patients to retain the same physician for future consultations. Offering services across primary care and chronic condition management, HealthTap is ideal for those seeking continuity in their healthcare journey.Hims & Hers: Privacy and Convenience
Hims & Hers specializes in personal care, particularly in areas that might traditionally be stigmatized, such as sexual wellness and mental health. While it does not accept insurance, the convenience of home delivery in discreet packaging makes it a solid choice for privacy-conscious individuals.Dr. B: Accessible Care for All
Dr. B diverges from the norm with its pay-what-you-can model, offering services even if patients cannot afford the flat consultation fee. This approach makes healthcare accessible to a broader audience, although the range of services may not be as extensive as other providers.MDLive: Insurance-Friendly Telehealth
MDLive provides mental health and urgent care services and is compatible with major insurance providers. It’s a solid pick for those looking to leverage their health insurance for telehealth visits. These are just a few of the notable highlights from CNET’s list, which also explores options like PlushCare, Doctor on Demand, and others, each offering unique features and benefits tailored to different aspects of healthcare. For further details and to learn more about these services, visit the full article on CNET.Revolutionizing Neurology: The AI Frontier
Revolutionizing Neurology: The AI Frontier

In a groundbreaking exploration of artificial intelligence’s (AI) transformative potential, a recent article published by Frontiers delves into how AI is reshaping the landscape of neurological care, particularly in emergency settings.
The Promise of AI in Neurology
AI technologies are being harnessed to revolutionize the diagnosis and management of neurological disorders. By integrating AI into various stages of patient care—from imaging diagnostics to personalized treatment plans—healthcare providers are witnessing a new era of medical innovation. According to the article, AI’s role in diagnostic imaging is particularly noteworthy, offering enhanced accuracy and speed in identifying conditions like stroke and traumatic brain injury.Advancements and Challenges
The article highlights recent advancements in AI applications within neurology, underscoring the potential for improved patient outcomes. However, the integration of AI into clinical practice is not without challenges. Ethical considerations, such as data privacy and algorithmic bias, pose significant hurdles. Moreover, practical barriers, including the need for infrastructure investment and clinician training, must be addressed to fully realize AI’s potential.Future Directions
Looking ahead, the article outlines prospective research areas and emerging trends in AI-assisted neurology. It suggests a focus on developing multimodal AI frameworks that combine imaging, genetic information, and clinical biomarkers for more comprehensive diagnoses. Additionally, the integration of AI with wearable devices and telemedicine platforms could offer continuous monitoring and real-time alerts, enhancing patient care.Recommendations for Clinical Practice
To facilitate the adoption of AI technologies in neurology, the article recommends several strategies:- Investing in infrastructure
- Improving data quality and diversity
- Fostering interdisciplinary collaboration
- Ensuring ethical and regulatory compliance
- Supporting ongoing research and development
This comprehensive review underscores AI’s potential to revolutionize neurological care, offering new hope for patients while emphasizing the need for responsible and equitable implementation.
Public Perception of Genetic Engineering: Insights Before and After the CRISPR Era
Public Perception of Genetic Engineering: Insights Before and After the CRISPR Era
The introduction of CRISPR-Cas9 in 2012 was a groundbreaking moment in the field of genetics, offering a more accessible method for precise genome modifications. This advancement has not only transformed genetic research but also ignited debates on the ethical implications of modifying human and animal genomes. There’s been a surge in both scientific and public interest, leading to extensive studies aimed at gauging public opinion on genetic engineering.A recent systematic review sheds light on the evolving public perceptions towards genetic modification both before and after CRISPR-Cas9’s debut. Conducted over a span of 35 years, the review chronicled public attitudes in various regions, including Asia, Europe, and North America, through an in-depth examination of questionnaire surveys. You can access the original study for more details here.
Before CRISPR, public discussions largely revolved around the potential medical applications of genetic engineering in humans, such as gene therapies aimed at curing genetic diseases. Conversely, the idea of genetic enhancement in humans was met with skepticism and often outright rejection. The public’s concern centered on ethical considerations, such as the naturalness of altering the human genome and potential societal impacts.
Post-CRISPR, while the overall acceptance of genome editing for treating diseases has increased, attitudes remain mixed regarding non-therapeutic enhancements. The differentiation between therapeutic and non-therapeutic uses remains significant; there’s strong support for treating severe genetic conditions but hesitance and ethical reservations persist regarding enhancements, such as altering intelligence or physical attributes.
The stance on genetically modifying animals similarly hinges on intended use—medical applications, such as producing organs for transplantation, receive higher acceptance compared to the use of genetic changes for food production.
The relationship between public awareness and attitude is complex. Generally, better-informed individuals tend to show greater support for genetic technologies, although this correlation is sometimes weak.
This comprehensive review also highlights methodological aspects of the surveys included, underscoring the need for standardized approaches to ensure consistency across future studies.
As genetic engineering technologies like CRISPR continue to advance, public consultation will be crucial, especially as these applications may directly impact everyday lives. This review underscores the importance of inclusive dialogue and informed policy-making to align technological innovation with societal values and expectations.
For more detailed insights, the original study and its supplementary materials offer further context and understanding of this evolving landscape.
Revolutionizing Real Estate: The Impact of IoT
Understanding the Impact of IoT on Real Estate
**IoT technology** is not just a buzzword; it’s a transformative force in real estate. With over 15 billion **IoT devices** currently in use, a number expected to reach 29 billion by 2030, the potential for innovation is immense. The Statista report highlights this explosive growth, emphasizing the increasing reliance on interconnected devices to enhance convenience, efficiency, and security in both residential and commercial properties.
The Business Benefits of IoT
The adoption of **IoT in real estate** brings numerous advantages. It offers cost efficiency by optimizing energy management systems, thereby reducing utility expenses. This not only provides affordable housing solutions but also addresses the pressing need for eco-friendly homes. According to CNBC, the U.S. faces a shortage of over 5 million affordable homes, and **IoT** could be key in bridging this gap.Moreover, **IoT** enhances incident management and safety. With smart sensors, potential hazards like fires or leaks can be detected early, ensuring swift response and minimizing damage. This proactive approach to safety is vital in today’s fast-paced world.
Environmental Sustainability and Innovation
**IoT’s role** in promoting environmental sustainability cannot be overstated. By enabling efficient resource consumption, **IoT** helps reduce the ecological footprint of buildings, catering to the growing demand for green homes. Additionally, innovative applications like virtual home hunting and smart decision-making tools are reshaping the real estate landscape, offering immersive experiences to potential buyers.
Real-World Examples of IoT in Action
Several companies are leading the charge in **IoT integration**. Samsung’s SmartThings Station, Eve Systems’ Matter-compatible accessories, and Shelly’s smart home automation devices are just a few examples of how **IoT** is being woven into the fabric of modern living. These innovations highlight the growing trend towards smarter, more connected homes.The collaboration between Latch and Honeywell, as well as Schneider Electric’s Easy Homes, further exemplifies the real-world application of **IoT** in enhancing property management and user experience.
Looking Ahead
As the **real estate sector** continues to embrace **IoT**, the potential for further innovation is boundless. With an anticipated market value of $2.5 trillion by 2029, according to the IoT Market Report, the integration of **IoT in real estate** promises to redefine how we live and work. The future is indeed bright for **smart homes** and **IoT-enabled real estate**.Key Property Investment Trends to Watch in 2025

Smaller Cities on the Rise
The dominance of major urban centers like New York and San Francisco is waning. According to Hajji, **smaller cities** such as Boise, Charlotte, and Tampa are experiencing rapid growth due to the shift towards **remote work**. This trend presents lucrative opportunities for investors seeking higher returns outside the traditional hotspots.Demand for Green Buildings
**Sustainability** is becoming a cornerstone of property investment. **Eco-friendly buildings**, which reduce energy consumption and environmental impact, are increasingly sought after. The Home Innovation Blog highlights the growing preference for sustainable homes, a trend echoed by government incentives for **green construction**.The Renting Revolution
With home prices continuing to rise, as noted in the Goldman Sachs Insights, **renting** is becoming more prevalent, especially among younger generations. **Build-to-rent (BTR) communities** are gaining traction, offering investors steady rental income and appealing amenities for tenants.Technological Transformations
The integration of **technology into property management** is revolutionizing the industry. **AI and automation** streamline operations, while **blockchain** enhances transaction security. Embracing these innovations can provide investors with a competitive edge.Interest Rates and Inflation
**Interest rates and inflation** remain critical factors in real estate investment. As borrowing costs rise, the market may slow, but real estate continues to be a robust hedge against inflation. Keeping a close watch on these economic indicators is crucial for making informed investment decisions.Opportunities in Affordable Housing
The demand for **affordable housing** is intensifying, with governments offering incentives for developments in this sector. **Public-private partnerships** are emerging as a solution to the housing crisis, presenting investors with a chance to achieve strong returns while contributing to social welfare.Conclusion
Navigating the property market in 2025 requires keen awareness of these evolving trends. Investors who adapt to changes in market dynamics, prioritize sustainability, and leverage technology will be well-positioned for success. As Johan Hajji emphasizes, staying ahead of the curve is essential for maximizing returns in this competitive environment.CMS Unveils Limited Digital Health Policies in Final Medicare Rule
CMS Reveals Limited Digital Health Policies in Final Medicare Rule
In a move that has drawn considerable attention just days before the 2024 presidential election, the **Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)** has released the final calendar year 2025 physician fee schedule (PFS) rule. This rule, which impacts **digital therapeutics**, **telehealth**, **rural health clinics**, and **opioid treatment programs**, underscores CMS’s limited authority in shaping digital health payment policies.
Digital Health Policies
CMS has finalized several digital health policies, as initially proposed in July’s draft rule. However, the offerings remain modest. New codes have been introduced for **digital therapeutics**, particularly aimed at mental healthcare. These changes mainly involve redefining existing codes to distinguish them from remote therapeutic monitoring codes. CMS’s authority in this area is limited, prompting a call for congressional action to create a new benefit category for digital therapeutics.
Telehealth Policies
With the expiration of **Medicare telehealth flexibilities** looming at the end of 2024, CMS has highlighted the necessity for Congress to extend key telehealth waivers. These waivers have significantly expanded telehealth services since 2020. Permanent coverage for audio-only visits and direct supervision via telehealth has been confirmed, yet geographical and origin site restrictions continue to pose challenges. For further details, you can refer to the original article.
Rural Health Clinics and Federally Qualified Health Centers
CMS has been striving to achieve payment parity for telehealth services compared to in-person services in **rural health clinics** and **federally qualified health centers**. While a special payment rate is applied for telehealth, CMS has opted to retain its current payment methodology for now, though reforms may be considered in the future.
Opioid Treatment Programs
The rule acknowledges the importance of telehealth in **opioid treatment programs**, especially for older Medicare beneficiaries who rely heavily on audio-only services. CMS will allow telehealth usage for periodic assessments, marking a step forward in addressing opioid use disorder through digital means.
For a comprehensive understanding of the finalized rule and its implications, visit the CMS Federal Register.
Conclusion
While CMS has made some progress, the agency emphasizes the need for congressional action to broaden and secure these developments. The future of **digital health policies** remains uncertain, with much depending on legislative support.
KBank’s Crypto Dilemma: Navigating Legislative Changes Amid IPO Plans
The financial landscape in South Korea is poised for a seismic shift as KBank, a major digital bank, grapples with a legislative curveball. The bank, which is heavily reliant on deposits from Upbit, Korea’s dominant cryptocurrency exchange, is facing a potential profit squeeze. The new Virtual Asset User Protection Act, set to take effect on July 19, 2024, mandates that banks must pay interest on crypto exchange deposits, a move that could severely impact KBank’s bottom line.
Currently, Upbit client deposits constitute a substantial 5 trillion won, approximately $3.6 billion, which is over 20% of KBank’s total client balances. While this figure reflects a decrease from previous levels, the impending requirement to pay interest could almost nullify the bank’s profits. The anticipated interest rate stands at 1%, a significant increase from the current 0.1% KBank pays. This change could necessitate an expenditure of around 50 billion won ($36 million), a figure alarmingly close to the bank’s profit margins.
The timing of this legislative change poses a particular challenge for KBank as it readies itself for an initial public offering (IPO). The potential financial strain from interest payments on crypto deposits might devalue the bank, complicating its IPO ambitions.
Bank Dependence on the Crypto Sector
KBank’s situation is reminiscent of Silvergate Bank in 2023, which faced a similar predicament due to its reliance on the crypto sector. Silvergate eventually opted for a voluntary shutdown after experiencing mass withdrawals post-crypto crash, despite having plans to repay all depositors. Similarly, Signature Bank, which had some exposure to the crypto industry, also faced collapse, although management denied that cryptocurrency was the cause.
In South Korea, no other bank shares KBank’s level of exposure to cryptocurrency exchange deposits, making its situation unique. As the banking sector braces for the implications of this new law, KBank stands at a crossroads, navigating the fine line between innovation and financial stability.
The Transformation of Healthcare: AI’s Role in Diagnostics and Personalized Medicine
From Data to Diagnosis
AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data is paving the way for a profound change in medical diagnostics. Khosla predicted that AI could take over up to 80% of standard medical tasks, reducing errors and biases in human diagnosis. This is particularly evident in fields like radiology and pathology, where AI’s proficiency in analyzing medical imaging allows for the early detection of diseases such as cancer, significantly improving treatment outcomes.
Moreover, AI’s integration into diagnostics is advancing global healthcare equity. By deploying AI-driven tools in under-resourced areas, high-quality diagnostics become accessible where specialized medical professionals are scarce, thus democratizing healthcare.
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatment with AI
AI’s role in personalized medicine is among its most promising applications. By analyzing genetic profiles and real-time health data, AI enables treatments tailored to individual patients. This shift from a one-size-fits-all approach to personalized care reduces adverse reactions and enhances treatment effectiveness. Research in Nature Humanities and Social Sciences Communications highlights AI’s role in driving precision healthcare, where treatments are increasingly customized based on biological markers, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices.
Additionally, AI is accelerating drug development. Pharmaceutical companies are leveraging AI to analyze large datasets from clinical trials, identifying potential new drug candidates more quickly and accurately than traditional methods. This faster drug discovery process could lead to more effective treatments reaching patients sooner, potentially transforming disease management and care.
AI in Patient Care Management
AI’s potential in patient care management is substantial. By continuously monitoring patient health data, AI systems can predict potential health issues and provide timely interventions, shifting healthcare from a reactive model to a proactive one. This proactive approach not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces long-term healthcare costs. AI-driven patient care management enables continuous monitoring, allowing healthcare providers to anticipate issues before they become critical.
AI-powered predictive analytics also play a crucial role in preventive care, identifying patients at risk of developing conditions like diabetes or hypertension long before symptoms appear. This early intervention strategy can prevent the onset of these diseases, significantly reducing the burden of chronic illnesses, which are among the leading causes of death worldwide.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
Integrating AI into healthcare is not without challenges, particularly concerning privacy, security, and ethics. AI systems require vast data to function effectively, raising concerns about data breaches and privacy. As AI systems make more autonomous decisions, ethical questions arise, such as who is responsible for incorrect diagnoses or treatment recommendations made by AI. These are complex issues that healthcare providers and regulators must address as AI becomes more prevalent in the industry (IQVIA).
The Nature article also underscores the ethical implications of AI in healthcare beyond data privacy and decision-making. AI’s use in patient care could lead to the dehumanization of healthcare, where decisions may become overly data-driven, potentially overlooking the nuances of human empathy and judgment. Balancing AI’s efficiency with the need for a human touch in patient care will be critical in the coming years.
Integrating AI
For healthcare leaders eager to embrace AI, a strategic, phased approach is recommended. Begin by identifying specific areas where AI can deliver immediate value, such as diagnostics or patient management, and launch pilot projects to test and refine these tools. It’s essential to build a multidisciplinary team that includes clinicians, data scientists, and ethicists to ensure that AI solutions are both effective and ethically sound. By focusing on small, manageable projects, AI implementation can be gradually scaled while minimizing disruption.
Equally important is addressing privacy, security, and ethical concerns upfront. Leaders should establish strong data governance frameworks to protect patient information and ensure transparency in how AI systems are used. Engaging with patients and stakeholders about the benefits and safeguards of AI is crucial for maintaining trust. Successfully integrating AI and enhancing patient care while upholding the values of compassion and ethics hinges on a culture of innovation and continuous learning.
A New Era of Healthcare
The future of healthcare lies in the seamless integration of AI technologies as partners in care, not just tools. AI is set to reshape healthcare by improving outcomes, reducing costs, and enabling personalized care. While the journey toward AI-driven healthcare is still in its early stages, the impact of these technologies is already being felt. As AI continues to advance, it will redefine the relationship between patients and healthcare providers, making care more efficient, effective, and personalized.
The Geography of Pandemic-Era Home Price Trends and Implications for Affordability
However, this growth was anything but uniform. A compelling new paper titled “The Geography of Pandemic-Era Home Price Trends and the Implications for Affordability” from the Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies reveals that rural and low-density areas experienced the most significant price increases. The shift toward remote work allowed families to explore housing options beyond high-cost urban centers, leading to a migration trend towards more affordable, less populated regions.
In particular, low-density suburbs of large cities, smaller markets, and rural areas witnessed a notable 36 percent increase in home prices, mirroring the national trend. In contrast, urban and moderate-density suburbs within large metropolitan areas—those with populations exceeding one million—saw more modest increases of 30 percent and 21 percent, respectively. This represents a marked departure from pre-pandemic patterns when price growth was more evenly spread across different regions.
Rural Areas: A Case of Dramatic Growth
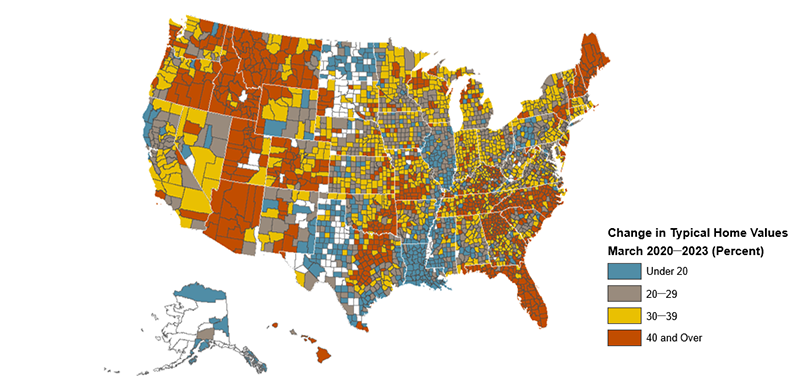
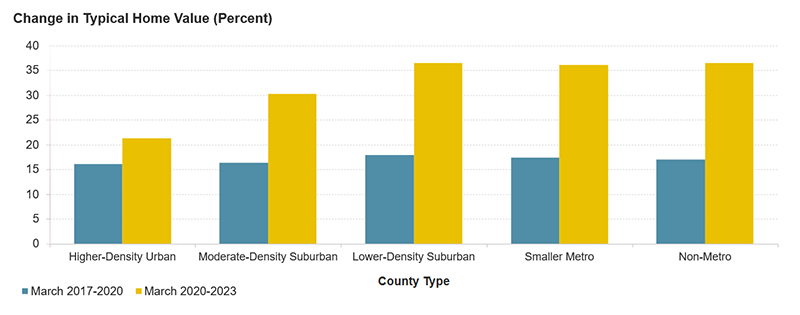 The disparity in growth is further highlighted by the fact that typical home values in 31 percent of non-metro counties surged by at least 40 percent following the pandemic. By comparison, only 18 percent of urban counties experienced growth beyond this threshold. Such disproportionate growth has intensified affordability issues, particularly in non-metro regions where the average home-value-to-income ratio has escalated from 2.5 to 3.9, approaching levels previously seen in urban counties before the pandemic.
The disparity in growth is further highlighted by the fact that typical home values in 31 percent of non-metro counties surged by at least 40 percent following the pandemic. By comparison, only 18 percent of urban counties experienced growth beyond this threshold. Such disproportionate growth has intensified affordability issues, particularly in non-metro regions where the average home-value-to-income ratio has escalated from 2.5 to 3.9, approaching levels previously seen in urban counties before the pandemic.
Affordability Challenges Intensify
 The rapid increase in home prices has significantly strained affordability in areas that were once considered more cost-effective. Rising interest rates have further compounded these affordability challenges, making homeownership an increasingly elusive goal for many. Whether these trends will persist depends on several factors, including ongoing remote work dynamics, regional affordability differences, and the capacity of housing supplies to meet new demand.
The rapid increase in home prices has significantly strained affordability in areas that were once considered more cost-effective. Rising interest rates have further compounded these affordability challenges, making homeownership an increasingly elusive goal for many. Whether these trends will persist depends on several factors, including ongoing remote work dynamics, regional affordability differences, and the capacity of housing supplies to meet new demand.
The original article on this topic can be found here.
AI in Healthcare: Transforming the Industry Today and Tomorrow
AI in Healthcare: Transforming the Industry Today and Tomorrow
In a world where technology is rapidly evolving, artificial intelligence (AI) is proving to be a game-changer in the healthcare sector. Once considered experimental, AI-powered tools are now making significant strides in improving patient outcomes, enhancing operational efficiency, and reducing costs. These advancements are not just theoretical; they are reshaping the very fabric of healthcare delivery. AI Tools Delivering Value Today
The impact of AI is evident across various facets of healthcare:
AI Tools Delivering Value Today
The impact of AI is evident across various facets of healthcare:
- Diagnostics: AI algorithms are enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. For instance, Google Cloud Healthcare is improving diagnostic speed and accuracy, while the AI-powered Butterfly Network’s handheld ultrasound device offers accessible point-of-care imaging.
- Drug Discovery: AI is accelerating drug development. Companies like Insilico Medicine use AI to identify promising drug candidates much faster than traditional methods.
- Personalized Medicine: AI-driven algorithms analyze patient data to craft personalized treatment plans. Tempus Labs leverages AI to provide tailored cancer treatments by analyzing genomic data.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: AI-enabled devices enhance chronic condition management. Livongo Health uses AI to monitor glucose levels and offer personalized coaching for diabetes management.
- Predictive Analytics: Health systems like Kaiser Permanente and Mayo Clinic employ AI-powered analytics to identify high-risk patients and prevent hospital readmissions.
- Administrative Efficiency: AI streamlines administrative tasks. Platforms like Cedar automate patient billing, while AI-powered chatbots improve patient engagement and communication.
- Predictive Healthcare: Advanced AI models will enable predictive healthcare, potentially predicting events like heart attacks days before they occur.
- Natural Language Processing for Clinical Documentation: AI will automate the transcription and summarization of medical records, unlocking insights from unstructured patient data.
- AI-Driven Telehealth: Integrating AI-powered diagnostic tools will enhance telehealth platforms, allowing for remote monitoring and early interventions.
- AI-Assisted Robotic Surgery: The integration of AI in robotic surgery will provide surgeons with real-time data analysis, optimizing surgical techniques and reducing recovery times.
- Precision Medicine and Gene Editing: AI-assisted technologies like CRISPR will enable targeted treatments for genetic diseases.
- Data Privacy and Security: Balancing privacy with utility is critical as AI systems require vast amounts of sensitive health data.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many healthcare providers operate on outdated infrastructure, complicating AI integration.
- Regulatory Approval: Regulatory bodies are still developing frameworks for AI in healthcare, which may slow adoption.
- Ethical Considerations: The “black box” nature of AI decision-making raises ethical concerns, especially in critical patient care decisions.
- Trust and Adoption: Building trust in AI-driven decisions is essential for widespread adoption by healthcare providers and patients.
- Healthcare Organizations: Start small with high-impact areas, invest in data infrastructure, and develop an AI roadmap.
- Healthcare Professionals: Embrace continuous learning, participate in AI pilot projects, and focus on AI-human collaboration.
- Patients: Stay informed about AI tools, ask questions about AI-driven care, and responsibly share data to improve AI healthcare tools.
Revolutionizing Surgical Training with VR and AI
Revolutionizing Surgical Training with VR and AI
In a groundbreaking study published by Nature, researchers have unveiled a novel approach to surgical training using a low-fidelity virtual reality (VR) simulator enhanced with artificial intelligence (AI) for objective assessment. This pioneering method is poised to transform how medical students acquire laparoscopic skills, offering a cost-effective and efficient alternative to traditional training models.The Evolution of Medical Education
For decades, medical education has relied on high-fidelity simulators, which, while effective, are often expensive and inaccessible to many training centers. The study, led by experts from the University of Pécs, aims to bridge this gap by developing a VR simulator that not only mimics the physical aspects of laparoscopic training but also incorporates AI to provide an objective evaluation of surgical skills.Objective Assessment: A Game Changer
The integration of AI into the VR simulator allows for a more precise and unbiased assessment of students’ performance. By utilizing AI algorithms, the system can detect errors and evaluate the efficiency of surgical tasks, providing detailed feedback that was previously only possible through subjective human evaluation. This advancement addresses a long-standing challenge in simulation-based education, as noted in previous studies by Theodoulou et al. (2018) and Evgeniou & Loizou (2013).Validation and Results
The study involved a cohort of medical students who were randomly assigned to train using either the traditional Fundamentals of Laparoscopic Surgery (FLS) box trainer or the newly developed VR simulator. Results showed no significant difference in the improvement of surgical skills between the two groups, highlighting the VR simulator’s effectiveness. Furthermore, the AI-based assessment proved to be as reliable as human evaluators, significantly reducing the time required for evaluations.Implications for the Future
The successful validation of this VR and AI approach opens the door for wider adoption in medical schools worldwide. It offers a scalable solution that can enhance the accessibility and quality of surgical training, particularly in resource-limited settings. As the demand for distance learning and personalized education grows, this innovative tool could play a crucial role in shaping the future of medical education.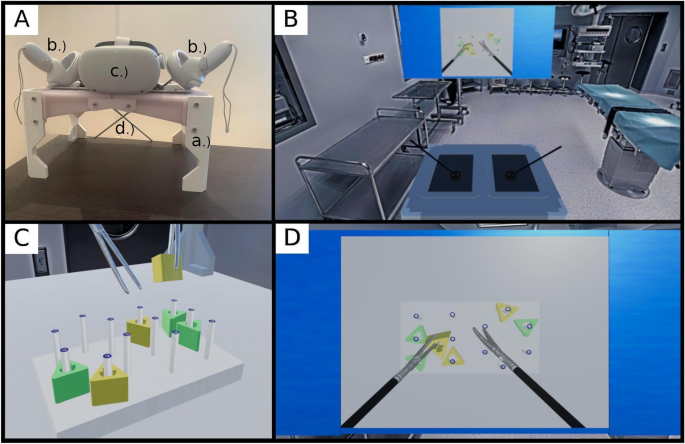
Conclusion
This study highlights the potential of combining VR and AI to revolutionize surgical training. As the medical field continues to evolve, embracing such innovative technologies will be essential in preparing the next generation of surgeons. For more detailed insights, the full study can be accessed at Nature’s website. “`AI and Machine Learning: Revolutionizing the Healthcare Industry
**AI** is already being integrated into **healthcare systems**, from developing new drugs and treatments to diagnosing complex conditions more efficiently and improving access to critical care. This is just the beginning of what **AI** can offer in a medical context.
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
**AI**, which involves using computers to perform tasks that traditionally required human intelligence, is transforming healthcare. When combined with **machine learning**, **AI** can process large datasets to learn and solve complex problems, much like a human would. This technology is being used across various medical fields, including **radiology**, **neurology**, and **emergency response services**, to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
According to Rohit Chandra, PhD, Cleveland Clinic’s Chief Digital Officer, “AI is no longer just an interesting idea, but it’s being used in a real-life setting.” He highlights that **AI** can now read **MRIs** and **X-rays** with greater accuracy than humans in certain cases, showcasing its advanced capabilities.
AI and Diagnostics
**AI’s role in diagnostics** is particularly promising. For conditions like broken bones, breast cancer, and brain bleeds, accurate diagnosis is crucial. **AI** assists radiologists by acting as a “second pair of eyes,” helping to identify diseases earlier and more accurately. Dr. Po-Hao Chen, a diagnostic radiologist at Cleveland Clinic, explains that **AI** works alongside radiologists to enhance diagnostic performance.
In breast cancer radiology, **AI** has shown significant promise. Dr. Laura Dean, a breast cancer radiologist, notes that **AI** assists in identifying subtle changes in breast tissue patterns, which can be crucial for early detection. Programs like ProFound AI are used to compare mammography images against learned datasets, highlighting areas of concern with a confidence level.
AI in Triage and Patient Management
**AI** is also improving patient care accessibility, especially in emergency situations. For instance, **AI** is used to triage medical cases, prioritizing those most critical. In stroke cases, where every minute counts, **AI** can analyze brain scans rapidly, expediting the care process. Programs like Viz.ai streamline communication among medical professionals, ensuring timely treatment.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
The future of **AI in healthcare** is particularly bright in the realm of research. Dr. Lara Jehi, Cleveland Clinic’s Chief Resource Information Officer, emphasizes the potential of **AI** in generating new knowledge and understanding diseases better. Her work in epilepsy surgery demonstrates how **machine learning** can improve decision-making and treatment outcomes.
As we continue to explore **AI’s possibilities**, ethical and safe use remains paramount. The World Health Organization has issued guidelines to ensure **AI’s responsible integration into healthcare**.
In conclusion, **AI** is poised to transform healthcare, offering unprecedented insights and efficiencies. As **AI technology** advances, it promises to enhance patient care and drive medical research to new heights.
Telemedicine: A Revolution in Healthcare
Telemedicine: A Revolution in Healthcare
In a world where technology is rapidly reshaping every facet of our lives, the healthcare sector is no exception. The recent review published in Cureus delves into the transformative role of telemedicine and telehealth, particularly in public healthcare. This narrative review highlights the integration of telehealth and telemedicine, their historical milestones, and how the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated their adoption.
Historical Milestones and Definitions
Telemedicine, a term coined in the 1970s, literally means “distance healing.” Its roots trace back to the early 1900s with the transmission of electrocardiograms over telephone lines. Fast forward to today, and telehealth encompasses a wide array of services, from video consultations to remote monitoring, making healthcare more accessible than ever before.
Methodologies and Discussions
The review underscores the importance of telemedicine in bridging the gap between healthcare providers and patients, especially in rural areas where access to medical facilities is limited. However, it also acknowledges the challenges, such as regulatory hurdles and infrastructure issues, that must be addressed to fully realize the potential of telehealth.
Benefits and Challenges
Telemedicine offers numerous benefits, including cost-effectiveness, improved access to healthcare, and enhanced emergency preparedness. Yet, challenges remain, such as ensuring patient information security and overcoming technical obstacles in remote areas. The review provides a balanced view, highlighting both the advantages and potential drawbacks of telehealth.
The COVID-19 Pandemic’s Influence
The pandemic has been a catalyst for telemedicine, forcing healthcare systems worldwide to adopt digital solutions quickly. This shift has proven beneficial, particularly for underserved communities, by providing continuous care without the need for physical visits. The review emphasizes the need for ongoing innovation to create user-friendly platforms that cater to both providers and patients.
Recent Technological Advancements
Recent advancements in telehealth technology, such as remote patient monitoring, are paving the way for more comprehensive healthcare solutions. These innovations are crucial, especially as the global population ages, necessitating efficient and cost-effective healthcare delivery.
Conclusion
Telemedicine and telehealth are no longer futuristic concepts but vital components of modern healthcare. As the review suggests, their role in enhancing healthcare access is undeniable, yet challenges persist. Addressing these barriers will be key to unlocking the full potential of telehealth and ensuring equitable healthcare for all.
Future of Construction: Trends Shaping the Industry by 2025
Revolutionizing Construction: Key Trends
The **construction sector** is witnessing a surge in innovative methodologies. Among these, modular construction is gaining momentum for its efficiency and sustainability. By prefabricating components in a controlled environment, developers can drastically cut down on-site construction time, a boon for sectors like multi-family housing and healthcare.
Another game-changer is 3D printing, which allows for the creation of building components layer by layer. This technology is set to revolutionize affordable housing and emergency shelters, offering significant reductions in waste and labor costs.
Technological Integration
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) is transforming project management. These technologies enable real-time data analysis, optimizing resource allocation and enhancing safety protocols. By 2025, AI is expected to be a staple in managing construction workflows.
Moreover, advancements in Building Information Modeling (BIM) are pivotal. By linking BIM with IoT devices, stakeholders can gain enhanced control over projects, from design to demolition, fostering unprecedented collaboration.
Sustainability and Smart Technologies
**Sustainability** is no longer a mere trend but a cornerstone of modern construction. The focus is on minimizing environmental impact through eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient systems. Initiatives like zero-carbon projects and recycled materials are becoming standard practice.
Smart building technologies are also at the forefront, with IoT sensors optimizing energy usage and security. As 5G networks expand, these buildings will self-regulate, reducing operational costs.
Challenges and Opportunities
While these advancements offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges. High initial costs, a skills gap, and regulatory hurdles can hinder widespread adoption. Overcoming these barriers is essential for the industry to fully capitalize on these innovations.
Leading the Way
Key players like Skanska and Bouygues Construction are at the forefront, leveraging green building practices and advanced technologies to enhance productivity and sustainability.
As we edge closer to 2025, the **construction industry** is poised for dramatic shifts. Those who embrace these changes will lead the way in shaping a smarter, more sustainable built environment.
The Legislative Battle for Telehealth: Navigating the Future of Virtual Care
As the clock ticks toward a December 31 deadline, a major House subcommittee is considering 15 bills aimed at expanding access to telehealth services. This legislative push is crucial as pandemic-era flexibilities face expiration, potentially affecting countless patients who have come to rely on virtual care.
The American Telemedicine Association has dubbed 2024 the “Super Bowl” of telehealth regulation, advocating for the permanent establishment of Medicare flexibilities introduced during COVID-19. According to FierceHealthcare, this regulatory showdown is critical for the future of telehealth.
The Push for Permanency
Healthcare systems and providers are urging lawmakers to secure permanent Medicare coverage for telehealth services. The absence of legislative action could result in a significant loss of access, particularly for vulnerable populations. Lee Schwamm, M.D., from Yale New Haven Health System, emphasized the need for permanent solutions, stating that telehealth allows for patient-centered care, especially when in-person visits pose challenges.
Prior to the pandemic, telehealth was often a cash-only service, inaccessible to many. However, the integration of virtual and in-person care has become a new standard, as highlighted by Eve Cunningham, M.D., from Providence health system. Telehealth now represents about 20% of ambulatory care visits at Providence, and its services extend to rural and underserved urban areas.
Legislative Proposals
Two significant bills, the CONNECT for Health Act and the Telehealth Modernization Act, aim to solidify telehealth flexibilities. These proposals seek to remove geographic restrictions, expand provider eligibility, and extend audio-only telehealth coverage. The American Hospital Association supports these measures, citing telehealth’s potential to address clinician shortages and enhance patient care.

Debate Over Costs and Quality
While telehealth has shown promise in improving chronic disease management and reducing emergency visits, concerns about increased healthcare spending remain. A previous extension was estimated to raise Medicare costs by over $2 billion. However, experts like Ateev Mehrotra, M.D., argue that the value of telehealth should guide policy decisions, despite modest spending increases.
Payment parity is another contentious issue. Some advocate for lower reimbursement rates for telehealth, while others, like Schwamm, caution against significant pay cuts that could discourage virtual care. The ongoing debate highlights the need for a balanced approach to telehealth reimbursement.
Fred Riccardi from the Medicare Rights Center urged for greater oversight before expanding Medicare coverage for telehealth. The organization emphasizes policies that increase access, promote health equity, and ensure high-quality care.
Conclusion
As lawmakers deliberate these legislative moves, the future of telehealth hangs in the balance. The decisions made in the coming months will shape the landscape of healthcare delivery, determining whether telehealth remains a core function or reverts to a limited service.
Harnessing AI in Healthcare: A New Era of Precision and Efficiency
The AI Revolution in Healthcare
The Cleveland Clinic, a pioneer in medical innovation, exemplifies the profound impact of AI in healthcare. According to Rohit Chandra, PhD, the Clinic’s Chief Digital Officer, **AI’s prowess** in interpreting medical images such as MRIs and X-rays often surpasses human capabilities. This advancement is not just theoretical; it is actively enhancing patient outcomes.AI in Diagnostics
**AI’s role** in diagnostics is particularly noteworthy. In breast cancer detection, tools like iCAD’s ProFound AI assist radiologists in identifying subtle changes in breast tissue, crucial for early detection. Similarly, AI-driven systems like Viz.ai are revolutionizing stroke triage, ensuring that critical cases receive immediate attention, thereby saving precious time and lives.Transforming Research and Patient Care
Beyond diagnostics, **AI is reshaping research methodologies**. The Discovery Accelerator, a collaboration between Cleveland Clinic and IBM, exemplifies how computational power can accelerate biomedical discoveries. By consolidating vast patient data, AI aids in refining treatment decisions and predictive models, notably in fields like epilepsy surgery.The potential of **AI extends** to managing tasks and improving patient services. AI-powered chatbots streamline patient interactions, while AI systems assist healthcare providers by capturing important notes during consultations, thus enhancing the overall patient experience.
Ethical Considerations and Future Prospects
As **AI continues to permeate healthcare**, ethical considerations become paramount. The Cleveland Clinic’s involvement in the AI Alliance underscores a commitment to advancing AI’s use in medicine responsibly. This global effort aims to ensure that AI’s integration into healthcare is both safe and ethical.The journey of AI in healthcare is just beginning, with its potential to revolutionize the field growing by the day. As Dr. Lara Jehi, Cleveland Clinic’s Chief Resource Information Officer, aptly puts it, AI offers a path forward that ensures no data is left behind, opening doors to new knowledge and improved patient care.
AI in Telemedicine Market on the Rise
AI in Telemedicine Market on the Rise
The AI in telemedicine market is set to experience a remarkable surge, growing from USD 19.4 billion in 2024 to an anticipated USD 156.7 billion by 2033. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.1%, driven by advancements in remote diagnostics, personalized treatments, and the integration of artificial intelligence across telemedicine platforms globally.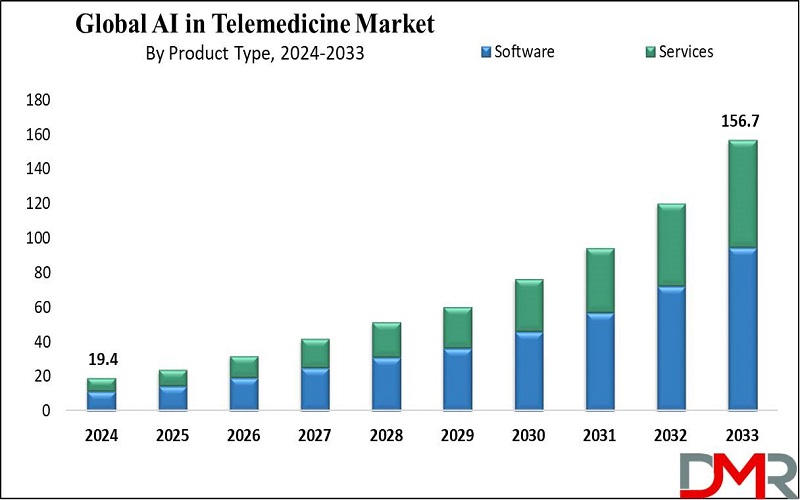
The Role of AI in Enhancing Telemedicine
AI technologies are revolutionizing telemedicine by enhancing remote diagnostics and personalized treatment plans. Tools such as virtual assistants and chatbots are streamlining patient interactions, reducing wait times, and improving diagnostic accuracy. These advancements are pivotal in driving the market’s growth, with teleconsultation services and IT advancements playing a significant role.Key Insights and Trends
- Market Growth: The global AI in telemedicine market is projected to expand by USD 132.7 billion between 2025 and 2033.
- Product Type: Software is expected to lead, accounting for 60.2% of revenue in 2024.
- Application Analysis: Virtual nursing assistants are anticipated to secure 26.4% of market revenue by the end of 2024.
- Regional Dominance: North America is forecasted to dominate with a 41.2% market share by 2024.
Technological advancements, including machine learning and natural language processing (NLP), are enhancing diagnostic accuracy and providing real-time data insights. The integration of cloud-based and edge AI technologies is further optimizing healthcare services.
Competitive Landscape
The market is highly competitive, with major players like Siemens Healthcare GmbH, IBM, and Cisco Systems Inc. leading the charge. These companies are driving innovation through technological advancements and addressing rising healthcare costs. Meanwhile, independent ventures are making significant strides by offering specialized services targeting specific medical conditions.Opportunities and Future Prospects
The AI in telemedicine market presents numerous opportunities, including enhanced diagnostic accuracy, streamlined efficiency, and cost reduction. These factors are expected to transform healthcare delivery, making telemedicine services more scalable and accessible.For more detailed insights, you can download the report excerpt or purchase the competition analysis dashboard.
Global Infrastructure Development: A New Frontier for Investment
Global Infrastructure Development: A New Frontier for Investment
In a world where infrastructure is the backbone of economic growth, the Global X Infrastructure Development Ex-U.S. ETF, known as IPAV, emerges as a promising investment vehicle for those looking to capitalize on the burgeoning international infrastructure sector. This ETF, listed on August 28, 2024, on the CBOE BZX, is designed to capture the growth potential of companies outside the United States that are poised to benefit from infrastructure advancements.
Driving Forces Behind the Infrastructure Boom
The revival of global infrastructure development is driven by a confluence of factors. As demographics shift and consumption increases, supportive government policies and investments become crucial. Moreover, the rise of emerging technologies such as generative AI and electric vehicles (EVs) are reshaping the landscape. These trends, while evident in the United States, are equally pronounced globally, creating a fertile ground for infrastructure investments.
- Technology and Investment: Major corporations like Alphabet, Amazon, and Microsoft are investing billions in infrastructure, focusing heavily on data centers to support AI growth.
- Geopolitical Shifts: Nations are increasingly focusing on energy security and supply chain resilience, driving infrastructure developments in domestic manufacturing.
- Urbanization and Demographics: The global population is rapidly urbanizing, necessitating new infrastructure to support social and economic mobility.
- Climate Change: The need for climate-resilient infrastructure is creating investment opportunities in sustainable projects.
Investing in the Future
The IPAV ETF targets companies involved in key sub-themes such as engineering and construction services, infrastructure transportation, raw and composite materials, construction equipment and products, and smart grid components. These sectors are vital as they provide the backbone for large-scale infrastructure projects, ranging from energy generation to telecommunications.

A Global Perspective
The international infrastructure theme is not just about traditional assets like roads and bridges. It also encompasses cutting-edge sectors like EV chargers and smart grids. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and aging infrastructure, the need for innovative solutions becomes more pressing. The IPAV ETF offers investors a chance to engage with these generational shifts, potentially reaping rewards from the intersection of social, demographic, technological, and energy consumption trends.
For more insights, read the full article on Global X ETFs.
Revolutionizing Medical Diagnostics with AI: A Leap Forward in Cytopathology
Revolutionizing Medical Diagnostics with AI: A Leap Forward in Cytopathology
In a groundbreaking advancement for medical diagnostics, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and computer vision is set to transform the analysis of cytopathological images. As reported in a recent article by Nature, this innovation is particularly crucial for developing countries where the shortage of medical professionals makes manual image analysis a daunting challenge.The Challenge of Manual Image Analysis
The interpretation of cytopathological images is a cornerstone of modern medical diagnosis. Yet, the sheer volume of image data makes it nearly impossible to manually identify and locate relevant cells. This issue is exacerbated in developing regions, where resources and trained personnel are scarce. The conventional methods of image segmentation demand extensive labeled data, which is often unavailable, leading to inefficiencies and inaccuracies.AI and Computer Vision: A Promising Solution
AI, through the lens of computer vision, offers a promising solution. By employing semi-supervised semantic segmentation, AI systems can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of image analysis. This method leverages a combination of labeled and unlabeled data, reducing the dependency on extensive human labeling. As a result, AI can significantly improve the diagnostic process, providing a more economical and effective option for cytopathology image diagnosis.Innovative Techniques and Developments
The article introduces a novel network architecture, RSAA (ResUNet-SE-ASPP-Attention), which integrates advanced modules like Squeeze and Excitation (SE), Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP), and Attention mechanisms. This architecture is designed to address the challenges of segmenting cellular pathology images, particularly in the detection of osteosarcoma. The RSAA model, along with the semi-supervised learning method RU3S, demonstrates a marked improvement in segmentation accuracy, even with limited labeled data.Impact on Developing Countries
For developing countries, where medical resources are limited, these advancements are game-changers. The ability to utilize unlabeled data effectively means that AI can alleviate the pressure on healthcare systems, enabling faster and more accurate cancer diagnoses. This development not only enhances the diagnostic workflow but also opens new avenues for timely and precise cancer detection.Conclusion
As we stand on the brink of a new era in medical diagnostics, the integration of AI and computer vision in cytopathology is a testament to the potential of technology to overcome significant healthcare challenges. This innovation, as highlighted in the Nature article, underscores the importance of continued research and development in AI-assisted medical diagnostics.The Expanding Threat Landscape in Healthcare
The Expanding Threat Landscape in Healthcare
In the rapidly evolving world of healthcare technology, the rise of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring has opened new frontiers for patient care. However, these advancements also widen the footprint for potential vulnerabilities, making data protection more crucial than ever. The original article from Health Data Management underscores the urgent need for healthcare organizations to prioritize secure data exchange and implement robust cybersecurity measures.
The Consequences of Data Breaches
The consequences of poor data security can be devastating. In 2019, over 500 breaches in the healthcare sector compromised millions of electronic health records. Such breaches often lead to stolen personal information, including Social Security numbers and medical histories, which can result in identity theft and insurance fraud. Beyond financial damage, these incidents erode patient trust, making individuals hesitant to share critical health information with their providers, thus hindering effective treatment.Challenges and Solutions in Secure Data Exchange
The complexity of healthcare systems presents unique challenges for secure data exchange. With vast amounts of sensitive information circulating, the industry is vulnerable to cyber threats, human error, and technical malfunctions. Implementing strong encryption methods for data at rest and in transit is essential. Encryption ensures that even if a breach occurs, the data remains unreadable without the proper keys. Regular network monitoring can help identify potential vulnerabilities before they escalate.Employee training is another critical solution. Human error accounts for a significant portion of data breaches in healthcare. Educating staff on best practices for data security can significantly reduce risks.
Keys to Successful Data Security
Healthcare organizations can enhance their data security efforts through several practical steps:- Conduct regular risk assessments to identify and address system vulnerabilities.
- Implement access controls to limit sensitive information access based on individual roles.
- Utilize two-factor authentication for an extra layer of security.
- Create a culture of cybersecurity awareness through ongoing employee training.

Prioritizing Data Security
As healthcare technologies advance, so must strategies for securing data. The rise of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring makes secure data exchange critical for maintaining patient confidentiality. By staying abreast of evolving cybersecurity threats and implementing robust measures, healthcare organizations can protect sensitive information and maintain patient trust.The original article serves as a clarion call for improved data protection, emphasizing the importance of a proactive approach to cybersecurity in healthcare.
By fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness and prioritizing data security, we can ensure trust in our healthcare systems while delivering quality care to patients.
Driverless Shuttles: A New Era of Mobility in Rural France
Driverless Shuttles: A New Era of Mobility in Rural France
In the picturesque yet sparsely populated region of Val de Drôme – Crest in southeastern France, a quiet revolution is underway. The deployment of self-driving shuttles is transforming the way residents navigate their rural surroundings. This initiative, launched in 2020, is part of a broader European effort to harness automated electric vehicles (EVs) as a viable public transport solution in areas where traditional services are often lacking.Yann Arnaud, director of responses to customer needs and innovation at the French insurance company MACIF, emphasized the potential of these shuttles during a conversation with Euronews. “We are trying to ensure that this is a new means of travel and mobility for people living in suburban or rural areas,” he stated, highlighting the project’s aim to reduce isolation and improve accessibility.
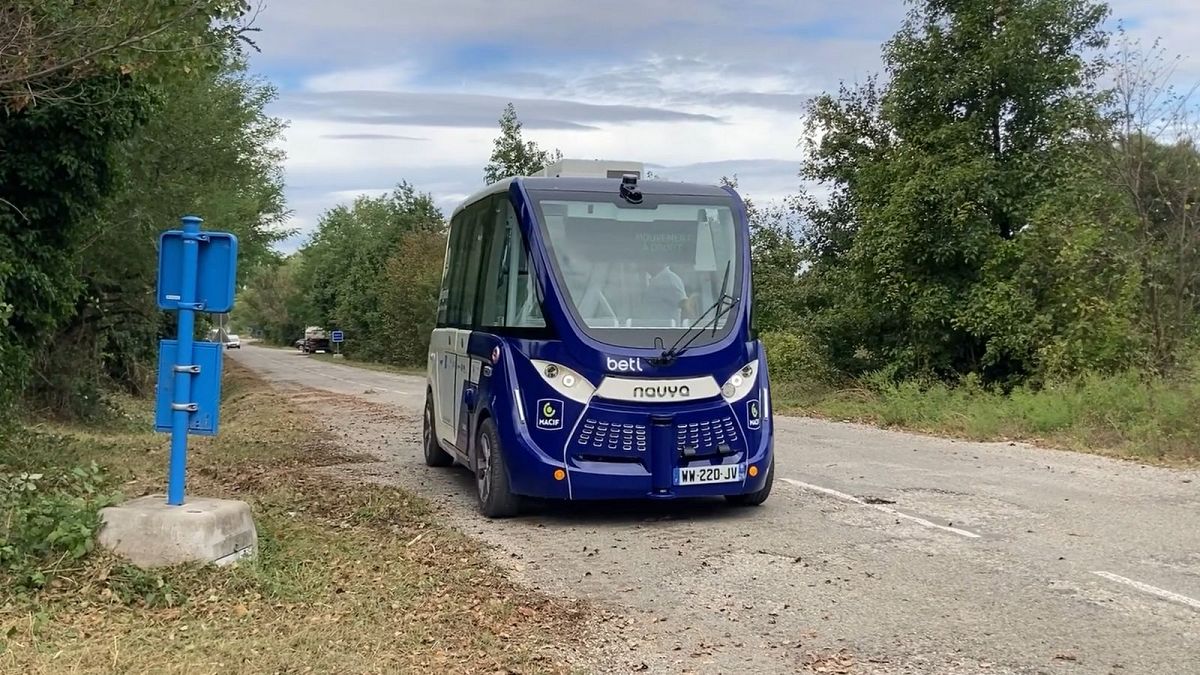

Technology and Safety
The shuttles operate on a predefined 5 km route, making seven stops over a 20-minute journey. A control operator oversees the operation to ensure safety. Benjamin Beaudet, general director at Beti, the operator of the automated shuttles, explained that the technology aligns with the European vision for automated vehicles. The shuttles “learn” their routes and compare real-time observations with pre-learned data to navigate safely.In contrast to American and Chinese companies like Waymo, Uber, and Tesla, which focus on self-driving taxis with flexible routes, the European approach prioritizes defined paths, enhancing safety and predictability.
Addressing Rural Needs
The introduction of these shuttles in Val de Drôme – Crest, where the population density is significantly lower than the national average, has been met with positive feedback. Residents appreciate the newfound mobility options, especially in areas where alternatives are limited. Arnaud noted, “The question of acceptability arises when you have the luxury of having other options. When you don’t have a choice, you’re very happy to have [the shuttle].”This sentiment underscores the potential of driverless vehicles to address mobility challenges in rural areas, particularly for the elderly and those without access to personal transportation.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the promising start, scaling these projects to permanent services remains a challenge. High costs, logistical hurdles, and technological requirements, as outlined in an Open Research Europe article, pose significant barriers. The EU has invested €159 million in research and innovation related to automated mobility since 2021, yet achieving commercial viability continues to be elusive.The success of initiatives like AVENUE and SHOW, which have conducted pilot projects across Europe, including in Crest, offers hope. However, transitioning from pilot programs to sustainable, everyday solutions requires overcoming substantial obstacles.
As Europe continues to explore the potential of automated vehicles, the experiences in rural France provide valuable insights into the future of mobility. With continued innovation and investment, driverless shuttles could become a cornerstone of public transport in remote areas, offering a greener, more accessible alternative to traditional car use.



































